Spot welding is a type of resistance welding that involves joining two metal surfaces together by applying heat and pressure to a specific area. This process creates a strong and durable bond, making it a popular choice in manufacturing and fabrication. The basic principle behind spot welding is to use an electrical current to generate heat at the weld point, softening the metal and allowing it to fuse together.
This is achieved by clamping the two metal pieces between copper alloy electrodes and passing a high electrical current through them for a brief period. The heat generated softens the metal, and the pressure applied by the electrodes forms the bond.
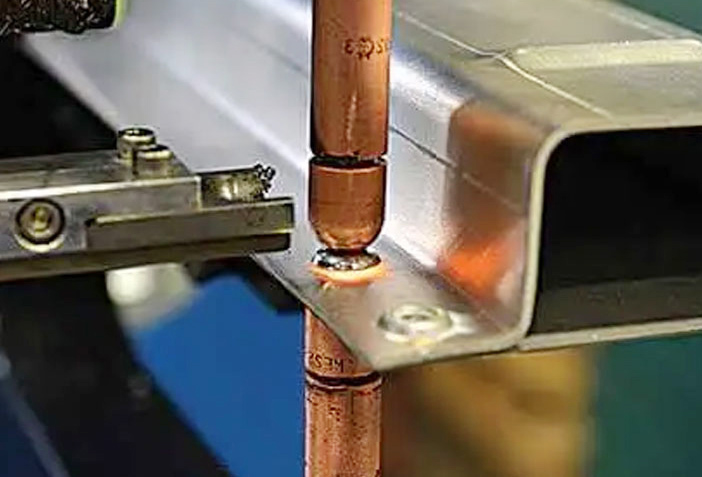
Photos by blvengineering.com.au
The key to the success of spot welding lies in the precision of the process. The duration and intensity of the electrical current, as well as the pressure applied, must be carefully controlled to ensure a consistent and reliable weld. The properties of the metal being welded, such as its thickness and composition, play a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of the spot welding process. As a result, spot welding requires specialized equipment and skilled operators to achieve the desired results.
Spot welding is commonly used in the automotive, aerospace, and electronic industries, where it is employed to join sheet metal components, wire harnesses, and various other metal parts. Its ability to create strong and uniform welds in a fraction of a second makes it an indispensable part of modern manufacturing processes. Moreover, the fact that it does not require additional materials such as filler metals or flux makes it a cost-effective and efficient welding method.
Spot Welding Equipment
The primary components of a spot welding system include the power supply, electrodes, and the workpiece. The power supply is responsible for providing the necessary electrical current to generate heat at the weld point. It must be capable of delivering a high current for a short duration to achieve the desired weld.
The electrodes, typically made of copper alloys to withstand high temperatures and pressure, are responsible for transmitting the electrical current to the workpiece and applying pressure to form the weld. The workpiece, consisting of the metal parts to be joined, must have clean and flat surfaces to ensure a successful weld.
In addition to these primary components, spot welding systems may also include control units to regulate the welding parameters, cooling systems to dissipate the heat generated during welding, and safety mechanisms to protect operators and the equipment.
The electrodes can take various forms, such as spot welding tips, seam welding wheels, or projection welding electrodes, depending on the specific application and requirements. Advancements in technology have led to the development of robotic spot welding systems, where robots are employed to perform the welding process with precision and efficiency.
The equipment used in spot welding varies in size and complexity, ranging from handheld spot welders for small-scale operations to fully automated welding cells for high-volume production. Regardless of the scale, the key components and their proper functioning are essential for achieving consistent and reliable spot welds. As such, regular maintenance and calibration of the equipment are necessary to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Advantages of Spot Welding
Spot welding offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in many manufacturing applications. Its high speed and efficiency allow for rapid production of welds, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing. The absence of additional materials such as filler metals and flux reduces the overall cost of welding, making spot welding a cost-effective process.
Spot welding produces minimal distortion and discoloration on the workpiece, resulting in clean and aesthetically pleasing welds. The strength and durability of spot welds make them ideal for applications where structural integrity is crucial.
Disadvantages of Spot Welding
Spot welding also has its limitations and disadvantages. One of the primary challenges is the limited accessibility of the weld point, particularly in situations where the workpiece has complex shapes or structures. This can make it difficult to achieve consistent and uniform welds across the entire surface. Spot welding is not well-suited for joining dissimilar metals or materials with significant differences in thickness, as it may result in uneven welds and potential quality issues.
Moreover, the need for precise control of welding parameters and the specialized equipment required for spot welding can pose challenges for small-scale or custom manufacturing operations.
Despite these limitations, the advantages of spot welding often outweigh its disadvantages, making it a versatile and widely used welding process across various industries. Its ability to create strong and reliable welds in a fast and cost-effective manner continues to make it an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing.
Applications of Spot Welding in Various Industries
Spot welding finds extensive use in a wide range of industries, thanks to its versatility and efficiency in joining metal components. In the automotive industry, spot welding is employed to assemble vehicle bodies, joining sheet metal panels, brackets, and reinforcements. The high-speed production capabilities of spot welding make it ideal for automotive manufacturing, where thousands of spot welds may be required to assemble a single vehicle. Additionally, the strength and durability of spot welds ensure the structural integrity of the vehicle, contributing to passenger safety and overall performance.
In the aerospace industry, spot welding is utilized in the fabrication of aircraft structures, fuel tanks, and various components. The ability to create strong and lightweight welds makes spot welding an attractive choice for aerospace applications, where the emphasis is on achieving high strength-to-weight ratios and maintaining structural integrity under extreme conditions. The efficiency of spot welding aligns with the stringent production timelines and quality standards prevalent in the aerospace sector.
The electronics industry also benefits from spot welding, where it is used to join wire harnesses, terminals, and other small metal components. The precise and localized heat generated during spot welding minimizes the risk of heat damage to sensitive electronic components, making it a suitable welding method for electronic assemblies. The speed and repeatability of spot welding contribute to efficient production processes in the electronics industry.
Beyond these industries, spot welding is also utilized in the fabrication of household appliances, furniture, metal enclosures, and a myriad of other products. Its ability to create strong and reliable welds in a fraction of a second makes it a valuable asset in modern manufacturing, contributing to the production of high-quality and durable goods across various sectors. As technology and materials continue to evolve, the applications of spot welding are expected to expand, further solidifying its position as a fundamental welding process.
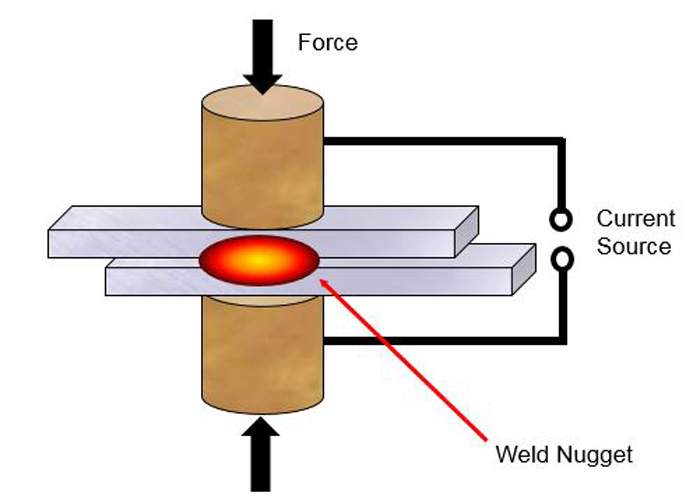
Photos by olympus-ims.com
Spot Welding Techniques and Best Practices
Successful spot welding relies on the application of proven techniques and best practices to ensure consistent and reliable welds. One of the critical factors in spot welding is the selection of appropriate welding parameters, including the welding current, welding time, and electrode force. These parameters are influenced by the type of metal being welded, its thickness, and the desired characteristics of the weld. The control and adjustment of these parameters are essential for achieving optimal weld quality and mechanical properties.
Another important aspect of spot welding is the preparation of the workpiece surfaces. Clean and flat surfaces are crucial for promoting good electrical contact and heat transfer during welding. Any contaminants, such as oils, paints, or oxides, should be removed from the surfaces to ensure proper fusion and strength of the weld. The alignment and clamping of the workpieces play a significant role in achieving uniform and consistent welds, particularly in applications involving multiple spot welds.
The maintenance and care of the welding equipment, including the electrodes, power supply, and control units, are also critical for the success of spot welding. Regular inspection, cleaning, and calibration of the equipment help prevent inconsistencies and defects in the welds. Operator training and adherence to safety protocols are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of spot welding systems. Proper handling of the equipment, as well as the use of personal protective equipment, minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures the well-being of the operators.
In addition to these technical aspects, advancements in spot welding technology, such as the integration of robotics and automation, have further enhanced the efficiency and precision of the process. Robotic spot welding systems offer the advantages of improved repeatability, accuracy, and productivity, making them well-suited for high-volume production environments. As industries continue to demand higher quality and efficiency, the adoption of advanced spot welding techniques and best practices is expected to play a crucial role in meeting these requirements.
Safety Measures in Spot Welding
Safety is paramount in spot welding operations, given the high electrical currents and temperatures involved in the process. Operators and maintenance personnel must adhere to strict safety guidelines to prevent accidents and injuries. One of the primary safety measures in spot welding is the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, welding helmets, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing. These items protect the operators from potential hazards such as electrical arcs, sparks, and heat generated during welding.
Additionally, proper ventilation and fume extraction systems are necessary to remove welding fumes and gases from the work area, ensuring a safe and healthy environment for the operators. Welding fumes may contain hazardous substances, and their inhalation should be minimized to prevent respiratory issues. Adequate ventilation also helps maintain the integrity of electronic equipment and sensitive components in the vicinity of the welding operation.
The maintenance and inspection of welding equipment, such as the power supply and electrodes, are essential for preventing malfunctions and potential safety hazards. Regular checks for damaged cables, loose connections, and overheating components help mitigate the risk of electrical accidents. Training programs for operators should emphasize safe handling of the equipment, proper setup of welding parameters, and emergency procedures in the event of equipment failure or accidents.
The implementation of safety protocols and the provision of comprehensive training not only protect the well-being of the operators but also contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of spot welding operations. By prioritizing safety measures, manufacturers can create a conducive working environment that promotes productivity and quality while minimizing the risk of workplace incidents.
Comparing Spot Welding with Other Welding Methods
Spot welding is just one of many welding methods available, each with its unique characteristics and applications. A common comparison is often made between spot welding and arc welding, another popular welding method. While spot welding is primarily used for joining thin metal sheets and components, arc welding is suitable for welding thicker materials and structures.
Arc welding utilizes an electric arc to generate the necessary heat for welding, and it offers greater versatility in terms of metal thickness and joint configurations. However, spot welding excels in speed and efficiency, making it the preferred choice for high-volume production and applications where rapid assembly is essential.
Another notable welding method is resistance welding, which encompasses spot welding as well as seam welding, projection welding, and flash welding. Resistance welding methods rely on the generation of heat through electrical resistance and pressure to create the weld. While spot welding focuses on localized welds, seam welding produces continuous welds along the length of a joint, making it suitable for applications such as sealing containers and fabricating tubes.
Projection welding is used to weld complex shapes and parts with varying thicknesses, offering flexibility in joining diverse components. Flash welding, on the other hand, is employed for welding larger sections and components, often in the construction and rail industries.
Furthermore, laser welding and ultrasonic welding are advanced welding techniques that offer distinct advantages in precision and control. Laser welding uses a focused laser beam to generate heat and create welds with minimal distortion, making it suitable for delicate and intricate components. Ultrasonic welding, on the other hand, utilizes high-frequency vibrations to create welds, particularly in plastics and non-ferrous metals. While these methods differ from spot welding in their approach, they share the common goal of creating strong and reliable bonds between materials.
When considering the choice of welding method, factors such as material properties, joint design, production volume, and required weld quality play a significant role in determining the most suitable approach. Manufacturers often employ a combination of welding methods to address diverse requirements and optimize the overall production process. The selection of the right welding method depends on a thorough understanding of the materials, design considerations, and production objectives.
Spot Welding in Automotive and Manufacturing Industries
The automotive industry stands as a prime example of the extensive use of spot welding in manufacturing. Vehicle bodies are typically assembled through a combination of spot welding and other welding methods, such as resistance spot welding and projection welding. The speed and precision of spot welding make it well-suited for joining the numerous sheet metal components that form the structure of a vehicle.
From body panels and frame components to brackets and reinforcements, spot welding plays a crucial role in creating a rigid and durable vehicle body. Moreover, advancements in robotic spot welding systems have further enhanced the efficiency and consistency of automotive assembly processes.
In addition to vehicle manufacturing, spot welding finds widespread use in the production of automotive components and subassemblies. Various automotive parts, such as exhaust systems, suspension components, and seating mechanisms, rely on spot welding for joining metal components with precision and strength. The ability of spot welding to create localized and uniform welds makes it an essential process in achieving the structural integrity and reliability required for automotive applications. The cost-effectiveness and speed of spot welding contribute to the overall competitiveness of automotive manufacturing.
Beyond the automotive industry, spot welding plays a significant role in the broader manufacturing sector. From the fabrication of appliances and consumer electronics to the production of industrial machinery and structural components, spot welding supports the creation of diverse products. Its ability to handle a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys, makes it a versatile choice for various manufacturing requirements. The high-speed production capabilities of spot welding align well with the demand for efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes across different industries.
As manufacturing technologies continue to evolve, spot welding is expected to remain a fundamental process in the production of goods. The integration of automation, robotics, and advanced materials will further enhance the capabilities and applications of spot welding, ensuring its relevance in meeting the evolving needs of modern manufacturing. By harnessing the advantages of spot welding, industries can continue to achieve high-quality, durable products that meet the demands of today’s markets.
Conclusion
Spot welding stands as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering a reliable and efficient method for joining metal components. Its ability to create strong and uniform welds in a fraction of a second makes it a preferred choice in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods. The precise control of welding parameters, the selection of appropriate equipment, and adherence to safety measures are essential for achieving consistent and
