As you dive into the art of stick welding, you’re about to embark on a journey that combines precision and finesse with raw power. Whether you’re drawn to the sizzle and spark of molten metal or craving the satisfaction of crafting something durable with your own hands, mastering stick welding is a rewarding endeavor. This article is your gateway to learning practical tips and tricks tailored for beginners, ensuring you start this adventure on the right foot.

Photos: weldingtipsandtricks
What is Stick Welding?
Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is a versatile and widely used welding process. It involves the use of an electric current to form an electric arc between the welding electrode and the metals to be joined. The heat of the arc melts the base metals and the electrode, creating a molten weld pool that solidifies to form a strong joint.
One of the key advantages of stick welding is its portability, making it suitable for outdoor and remote welding applications. It is well-suited for welding thick and rusty materials, making it a popular choice in construction, fabrication, and repair work.
Mastering stick welding requires a solid understanding of the equipment, safety precautions, electrode selection, and welding techniques. By getting a grasp of these fundamentals, beginners can set themselves up for success in their welding endeavors.
Essential Equipment for Stick Welding
Before diving into stick welding, it’s crucial to gather the necessary equipment to ensure a smooth and safe welding experience. The essential equipment for stick welding includes a welding machine, welding electrodes, welding helmet, welding gloves, welding jacket, chipping hammer, wire brush, and welding clamps.
The welding machine, or welder, is the heart of the stick welding setup. It generates the electric current needed to create the welding arc. When choosing a welding machine, consider factors such as amperage range, duty cycle, and portability to suit your specific welding needs. Additionally, investing in high-quality welding electrodes is essential for achieving strong and clean welds. The type and diameter of the electrodes should be selected based on the material being welded and the desired welding characteristics.
Safety Precautions for Stick Welding
Safety should always be the top priority when engaging in stick welding. As a beginner, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the safety precautions to protect yourself and others from potential hazards. Before starting any welding operation, ensure that your work area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes and gases. It’s advisable to weld in a designated welding area with proper ventilation or to use exhaust fans and fume extractors to remove welding fumes.
In addition to proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential to safeguard against welding hazards. A welding helmet with a clear and durable visor is crucial for protecting your eyes and face from the intense light and sparks produced during welding. Welding gloves, made of heat-resistant materials, shield your hands from burns and sparks, while a welding jacket provides protection for your upper body. Proper footwear and clothing should also be worn to prevent burns from hot metal and sparks.
Choosing the Right Electrodes for Stick Welding
Selecting the right electrodes is a critical aspect of stick welding, as it directly impacts the quality and characteristics of the weld. Electrodes come in various types, each designed for specific welding applications and metal types. The American Welding Society (AWS) classification system provides a standardized way to identify and select electrodes based on their properties and intended use.
The choice of electrodes is influenced by factors such as the type of base metal, welding position, desired weld characteristics, and the welding environment. For example, E6010 electrodes are well-suited for deep penetration and welding in challenging positions, while E7018 electrodes are known for their strong and clean welds, making them suitable for structural welding.
Setting Up Your Stick Welding Machine
Properly setting up your stick welding machine is essential for achieving consistent and high-quality welds. Start by ensuring that the welding machine is connected to a reliable power source and that all cables and connections are secure. Adjust the welding machine settings, including the amperage and polarity, based on the electrode type and the thickness of the base metal.
It’s important to strike a balance between the welding current and the travel speed to achieve the desired weld bead profile and penetration. Practice adjusting the welding machine settings on scrap metal before beginning your actual welding project to familiarize yourself with the machine’s controls and to fine-tune the settings for optimal welding performance.
Tips for Achieving Quality Stick Welds
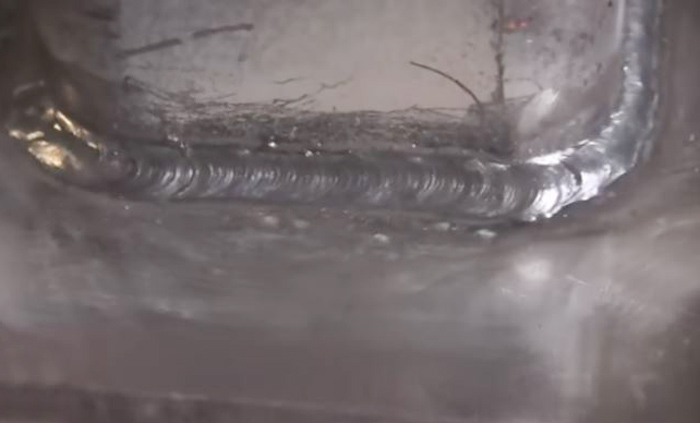
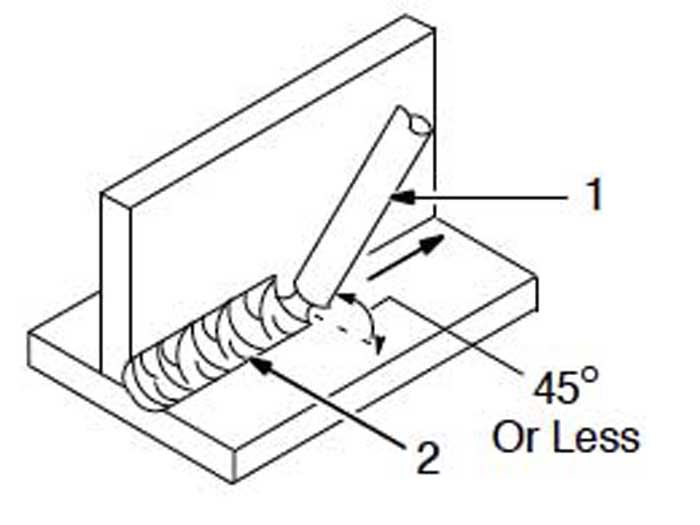
As a beginner in stick welding, focusing on the fundamentals and practicing proper welding techniques is key to achieving quality welds. Maintaining a consistent arc length between the electrode and the workpiece is crucial for producing uniform and sound welds. Too long of an arc length can cause spatter and incomplete fusion, while a short arc length may lead to electrode sticking and rough weld appearances.
Additionally, mastering the proper travel speed and weaving technique contributes to the overall appearance and strength of the weld. Experiment with different travel speeds and weaving patterns to find the optimal technique for the specific welding application. Continuous practice and attention to detail will refine your welding skills and lead to improved weld quality.
Photos: caa-99.top
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Stick Welding
In the pursuit of stick welding proficiency, it’s important to be aware of common mistakes and pitfalls that can compromise the quality of your welds. One prevalent mistake is improper electrode angle and manipulation, leading to inconsistent weld bead shapes and inadequate penetration. Maintaining a consistent and appropriate electrode angle is crucial for achieving uniform welds with proper fusion.
Another common mistake is neglecting the cleanliness of the base metal and the welding electrode. Contaminants such as rust, paint, and grease can negatively impact the quality of the weld, leading to defects and weak joints. Thoroughly clean the welding surfaces and remove any contaminants before beginning the welding process to ensure strong and reliable welds.
Advanced Stick Welding Techniques
Beyond the foundational principles of stick welding, there are advanced techniques that experienced welders employ to further enhance their welding capabilities. One such technique is known as multipass welding, which involves making multiple welding passes to fill in grooves or gaps in the base metal. This technique is commonly used in structural welding and pipe welding to create strong and structurally sound joints.
Another advanced stick welding techniques is the use of backing bars or backer strips to support the molten weld metal and prevent distortion in the base metal. Backing bars are particularly useful when welding thicker materials and can help achieve full penetration and uniform weld profiles. These advanced techniques require a deeper understanding of welding processes and materials, making them valuable skills for welders looking to tackle complex welding projects.
Stick Welding Troubleshooting
In the course of stick welding, encountering welding imperfections and defects is not uncommon. Understanding how to troubleshoot and rectify these issues is essential for maintaining welding quality. Some common welding imperfections include porosity, undercut, spatter, and lack of fusion. These issues can stem from improper welding techniques, electrode selection, or machine settings.
When facing welding imperfections, it’s important to identify the root cause and make the necessary adjustments to mitigate the issue. For example, adjusting the welding parameters or changing the electrode type may address issues such as spatter and lack of fusion. Continuous practice, coupled with the ability to troubleshoot welding imperfections, will sharpen your stick welding skills and bolster your confidence in tackling diverse welding challenges.
Final Thoughts
Stick welding offers a gateway to the world of metalworking, providing a blend of technical prowess and artistic expression. By understanding the fundamentals of stick welding, selecting the right equipment and electrodes, prioritizing safety, and honing essential welding techniques, beginners can lay a solid foundation for their welding journey. While mastering stick welding takes time and practice, the rewards of creating strong and enduring welds are well worth the effort.
As you embark on your stick welding endeavors, remember that continuous learning and hands-on experience are the cornerstones of welding mastery. Embrace the challenges, learn from your mistakes, and celebrate the progress made with each successful weld. With the tips and tricks shared in this article, you’re equipped to embark on your stick welding adventure with confidence and enthusiasm, ready to forge metal masterpieces with every strike of the arc.
This comprehensive guide to stick welding for beginners aims to demystify the welding process and provide actionable insights to empower budding welders. By delving into the nuances of stick welding, from equipment setup to advanced techniques, this article serves as a valuable resource for those venturing into the world of metal fabrication and welding. Whether pursuing stick welding as a hobby or a profession, the knowledge and skills gained from this guide set the stage for a fulfilling and successful welding journey.
