As you begin venturing into the world of metalworking, plug welding can be your go-to technique for efficiently joining sheet metal. Whether you’re a seasoned fabricator or a DIY enthusiast, mastering this method is essential. Creating a strong and durable bond between metal sheets, plug welding offers structural integrity without compromising the material’s appearance. Through this article, we’ll delve into the nitty-gritty of plug welding, exploring the tools, techniques, and best practices to elevate your metalworking proficiency.
Photos by mig-welding.co.uk
Fundamentals of Plug Welding
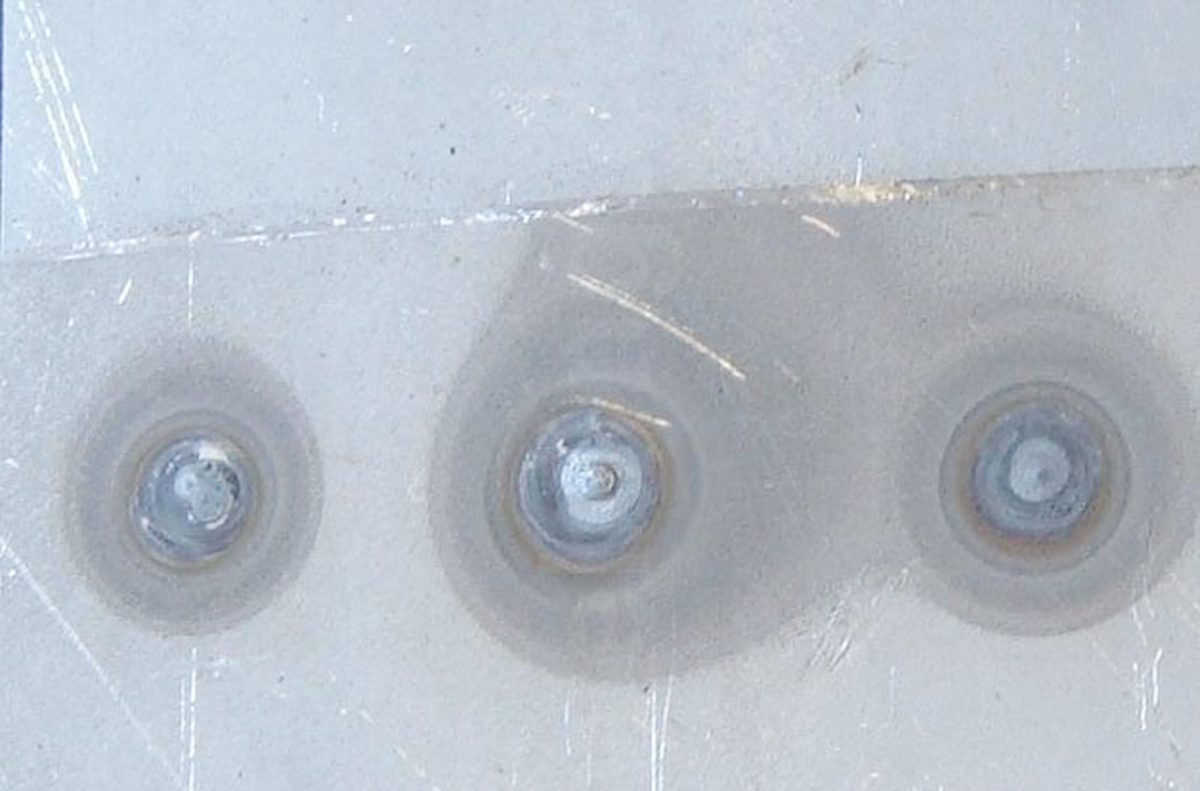
Understanding the fundamentals of plug welding is crucial for achieving seamless and reliable results. Plug welding involves joining two overlapping sheets of metal by welding through the top sheet to the bottom sheet, creating a strong and concealed bond. This method is commonly used in automotive and sheet metal fabrication, providing a clean and unobtrusive finish. By comprehending the principles of plug welding, you will be equipped to execute precise welds with confidence, ensuring the structural integrity of your metalwork projects.
Mastering the technique of plug welding requires a keen understanding of metal fusion and heat distribution. As you embark on your plug welding journey, familiarize yourself with the behavior of different metals under heat and the optimal welding conditions for various sheet thicknesses. This foundational knowledge will serve as the cornerstone for achieving professional-grade plug welds and elevating your metalworking prowess.
Plug welding not only ensures a strong bond between metal sheets, but it also offers a visually appealing finish by minimizing the visibility of welds on the surface. This makes it an ideal choice for projects where aesthetics and structural integrity are equally important. As we delve deeper into the art of plug welding, you will uncover the intricacies of this technique and gain insights into its versatile applications across diverse metalworking endeavors.
Advantages of Plug Welding Sheet Metal
Plug welding boasts several advantages that make it a preferred method in sheet metal fabrication. One of the primary benefits is its ability to create strong and seamless joints without the need for additional fasteners or visible weld beads. This results in a clean and unobtrusive finish, making plug welding an ideal choice for applications where aesthetics play a significant role.
Additionally, plug welding offers structural integrity by distributing the load across the joint, effectively reinforcing the connection between metal sheets. This makes it an invaluable technique in automotive repair, custom metalwork, and industrial fabrication, where the durability of the welds is paramount. Furthermore, plug welding minimizes the risk of corrosion by maintaining a continuous surface on the top sheet, preventing moisture and debris from accumulating in the joint.
The versatility of plug welding allows for creative freedom in metalworking projects, enabling fabricators to achieve seamless joins in intricate designs and complex assemblies. Whether you’re crafting custom panels, repairing bodywork, or fabricating artistic metal sculptures, plug welding empowers you to achieve professional-grade results with precision and finesse.
Tools and Equipment for Plug Welding Sheet Metal
To embark on your plug welding journey, you will need a set of essential tools and equipment to ensure seamless execution and optimal results. The following are the key components required for proficient plug welding:
Welder: A MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welder or a spot welder is typically used for plug welding. Ensure that your welder is equipped with the necessary settings and accessories to accommodate the thickness of the metal sheets you will be working with.
Clamps or Magnets: Securely holding the metal sheets in position is crucial for achieving precise plug welds. Utilize clamps or magnets to ensure the proper alignment and overlap of the sheets before initiating the welding process.
Grinders and Abrasives: Preparing the metal surfaces prior to plug welding is essential for ensuring optimal weld penetration and adhesion. Use grinders and abrasives to clean and smoothen the welding area, removing any contaminants or surface imperfections that may affect the quality of the weld.
Protective Gear: Prioritize welding safety by donning appropriate protective gear, including welding gloves, a welding helmet with a darkened visor, and flame-resistant clothing. Protecting yourself from potential hazards is paramount when engaging in metalworking activities.
Measuring Tools: Accurate measurements and precise positioning are essential for successful plug welding. Utilize measuring tools such as rulers, squares, and calipers to ensure the proper alignment and overlap of the metal sheets before initiating the welding process.
By assembling the necessary tools and equipment, you’ll be well-prepared to embark on your plug welding endeavors, ensuring a seamless and professional approach to joining metal sheets with precision and finesse.
Preparing the Sheet Metal for Plug Welding Sheet Metal
Before initiating the plug welding sheet metal process, it’s imperative to prepare the sheet metal to ensure optimal weld quality and structural integrity. The following steps outline the essential preparations for achieving successful plug welds:
Cleaning the Metal Surfaces: Thoroughly clean the welding area on both metal sheets to remove any rust, paint, or contaminants that could impede the welding process. Use a wire brush or abrasive pad to achieve a clean and bare metal surface for seamless weld penetration.
Ensuring Proper Fit and Overlap: Align the metal sheets to achieve the desired joint configuration, ensuring that they overlap to the specified dimensions for plug welding. Utilize clamps or magnets to secure the sheets in position, maintaining the required overlap for the welding process.
Marking the Weld Locations: Mark the precise locations where the plug welds will be executed on the top metal sheet. Utilize a scribe or marker to clearly indicate the weld points, ensuring accuracy and consistency in the placement of plug welds across the metal surface.
Surface Contouring and Preparation: If the metal sheets have irregular or uneven surfaces, consider contouring or leveling the welding area to ensure uniform contact between the sheets. This step is crucial for achieving seamless plug welds and preventing gaps or inconsistencies in the joint.
By meticulously preparing the sheet metal for plug welding, you will establish a solid foundation for executing precise and durable welds, setting the stage for professional-grade results in your metalworking projects.
Step-by-Step Guide to Plug Welding Sheet Metal
Mastering the step-by-step process of plug welding is essential for achieving seamless and durable joins between metal sheets. The following guide outlines the sequential stages of plug welding sheet metal, empowering you to execute this technique with precision and confidence:
Positioning the Metal Sheets: Align the metal sheets to achieve the desired overlap, ensuring that the top sheet overlaps the bottom sheet at the designated welding locations. Use clamps or magnets to secure the sheets in position, maintaining the required overlap for plug welding.
Initiating the Welder: Power up the MIG welder or spot welder, ensuring that it is configured with the appropriate settings for the metal thickness and welding conditions. Verify that the welding equipment is in optimal working condition before proceeding with the welding process.
Executing the Plug Welds: Position the welding gun or electrode at the marked weld locations on the top metal sheet. Initiate the welding process by delivering short bursts of welding current to penetrate through the top sheet and fuse with the bottom sheet. Ensure uniform and consistent penetration to create strong and reliable plug welds.
Monitoring Weld Penetration: As you execute the plug welds, monitor the penetration and fusion of the metal sheets to verify the quality of the welds. Ensure that the welds exhibit complete fusion and adhesion between the top and bottom sheets, indicating a robust and reliable joint.
Cooling and Inspection: Allow the plug welds to cool naturally before conducting a thorough inspection of the welded area. Inspect the welds for uniformity, integrity, and proper fusion, ensuring that they meet the desired quality standards for structural integrity and visual appeal.
By following this comprehensive guide to plug welding, you will gain the expertise to execute seamless and professional-grade welds, elevating your metalworking capabilities and achieving exceptional results in your fabrication projects.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Plug Welding Sheet Metal
While mastering plug welding sheet metal, it’s essential to be aware of common mistakes and pitfalls that can compromise the quality and integrity of your welds. By recognizing and avoiding these errors, you will elevate your plug welding proficiency and ensure consistent and reliable results in your metalworking endeavors. The following are common mistakes to steer clear of when engaging in plug welding:
Inadequate Surface Preparation: Neglecting to thoroughly clean and prepare the metal surfaces before plug welding can lead to poor weld penetration and adhesion. Ensure that the welding area is free from contaminants, rust, and paint, facilitating optimal fusion and structural integrity in the welds.
Misalignment of Metal Sheets: Improper alignment and overlap of the metal sheets can result in weak and inconsistent plug welds. Take the time to ensure that the sheets are accurately positioned and securely clamped before initiating the welding process, minimizing the risk of joint irregularities.
Excessive Welding Current: Applying excessive welding current can lead to burn-through or distortion of the metal sheets, compromising the quality of the plug welds. Adhere to the recommended welding settings and techniques to achieve controlled penetration and fusion, preventing overheating and material damage.
Insufficient Weld Penetration: Failing to achieve adequate penetration through the top metal sheet can result in weak and superficial plug welds. Monitor the welding process closely to ensure that the current penetrates through the top sheet and fuses with the bottom sheet, creating a robust and durable joint.
Neglecting Post-Weld Inspection: After completing the plug welding process, neglecting to conduct a thorough inspection of the welds can lead to undetected defects or inconsistencies. Inspect the welds for uniformity, adhesion, and structural integrity, ensuring that they meet the desired quality standards for your metalworking projects.
By steering clear of these common mistakes and maintaining a meticulous approach to plug welding, you’ll enhance the quality and durability of your welds, setting the stage for professional-grade results in your sheet metal fabrication endeavors.
Tips for Achieving Strong and Clean Plug Welding Sheet Metal
Elevating your plug welding proficiency involves implementing best practices and techniques that yield strong and clean welds with precision and finesse. The following tips are instrumental in achieving exceptional plug welds and enhancing the overall quality of your metalworking projects:
Optimize Welding Settings: Fine-tune the settings on your MIG welder or spot welder to align with the thickness and material composition of the metal sheets. Adjust the welding current, voltage, and wire feed speed to achieve controlled penetration and uniform fusion in your plug welds.
Maintain Consistent Welding Technique: Adhere to a steady and consistent welding technique when executing plug welds, ensuring uniform penetration and fusion across the welding area. Avoid abrupt movements or erratic welding patterns that can result in irregular welds and compromised structural integrity.
Minimize Distortion and Warping: To prevent distortion and warping of the metal sheets during plug welding, implement techniques such as tack welding or utilizing heat sinks to dissipate excess heat. By mitigating the risk of material deformation, you will achieve clean and seamless plug welds with minimal impact on the overall metalwork.
Utilize Backing Bars for Support: When plug welding thin or lightweight metal sheets, consider using backing bars to provide support and reinforcement during the welding process. This helps maintain the flatness and integrity of the metal sheets, facilitating consistent and durable plug welds.
Conduct Post-Weld Cleaning and Finishing: After completing the plug welding process, conduct thorough cleaning and finishing of the welded area to remove any spatter or surface imperfections. Utilize grinders, abrasives, and metal finishing techniques to achieve a clean and visually appealing finish on the welds.
By incorporating these tips into your plug welding practices, you’ll elevate the quality and integrity of your welds, setting a high standard for precision and craftsmanship in your sheet metal fabrication endeavors.
Best Practices for Finishing and Inspecting Plug Welding Sheet Metal
Completing the plug welding process is only the initial step in achieving professional-grade results in sheet metal fabrication. Implementing best practices for finishing and inspecting plug welds is essential for ensuring structural integrity and visual appeal in your metalworking projects. The following practices are instrumental in elevating the overall quality of your plug welds:
Grinding and Smoothing Weld Beads: After completing the plug welds, utilize grinders and abrasives to smooth and contour the weld beads, achieving a visually clean and seamless finish on the metal surface. This step enhances the aesthetic appeal of the welds and minimizes their visibility on the finished metalwork.
Conducting Visual Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the plug welds for uniformity, adhesion, and fusion, ensuring that they meet the desired quality standards for structural integrity. Verify that the welds exhibit complete penetration and minimal surface irregularities, indicating a robust and reliable joint.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Consider implementing non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing or dye penetrant inspection to assess the internal integrity of the plug welds. NDT techniques provide valuable insights into the quality and consistency of the welds, ensuring that they meet stringent performance standards.
Corrosion Protection and Coating: Apply appropriate corrosion protection measures to the welded area, safeguarding the plug welds from environmental degradation and moisture exposure. Utilize primers, sealants, or protective coatings to enhance the longevity and durability of the welds in diverse operating conditions.
Documentation and Quality Assurance: Maintain comprehensive documentation of the plug welding process, including weld specifications, inspection reports, and quality assurance records. This ensures traceability and accountability in the fabrication process, demonstrating adherence to industry standards and best practices.
By embracing these best practices for finishing and inspecting plug welds, you’ll elevate the overall quality and reliability of your metalwork, setting a high standard for craftsmanship and precision in sheet metal fabrication.
Plug Welding vs Other Welding Techniques
In the realm of metalworking, plug welding stands out as a versatile and efficient technique for joining sheet metal. However, it’s essential to understand how plug welding compares to other welding methods, providing insights into its unique advantages and applications. Contrasting plug welding with alternative techniques sheds light on its distinct characteristics and reinforces its significance in diverse metalworking scenarios.
When it comes to welding, there are a ton of different techniques out there. And honestly? It can get a little overwhelming. But one technique that’s worth considering is plug welding. Basically, with plug welding, you’re attaching two pieces of metal by filling a drilled hole with molten metal. The result? A strong, secure bond.
One of the big benefits of plug welding is that it’s super efficient—you don’t have to do any prep work like you might with other welding techniques. And not only that, but plug welding can be used in a variety of different applications, from car repair to construction. Of course, there are also other welding techniques out there that have their own advantages, but if you’re looking for a no-fuss method that can get the job done, plug welding is definitely worth a look.
Conclusion
Plug welding is a commonly used technique for joining sheet metal, offering several advantages such as increased strength and improved structural integrity. However, it is not without its disadvantages, including the potential for distortion and the need for precise preparation. To ensure successful plug welding, it is crucial to avoid common mistakes such as inadequate surface cleaning and improper electrode selection. By understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and common mistakes of plug welding, fabricators can effectively utilize this technique to achieve strong and durable sheet metal joints.
