A mig welder is a welding machine that uses lead wire to produce welds on steel, ferrous and non-ferrous materials. A tig welder, on the other hand, is a welding machine that uses Tig Welding Rods to produce welds on all types of metals. Both of these welding machines are similar in many ways, but they also have key differences that you should consider before making a purchase. Knowing these differences will help you choose the right welder for your needs and avoid any future buyer’s remorse down the road. In this article we will discus about the difference between a mig welder and a tig welder.
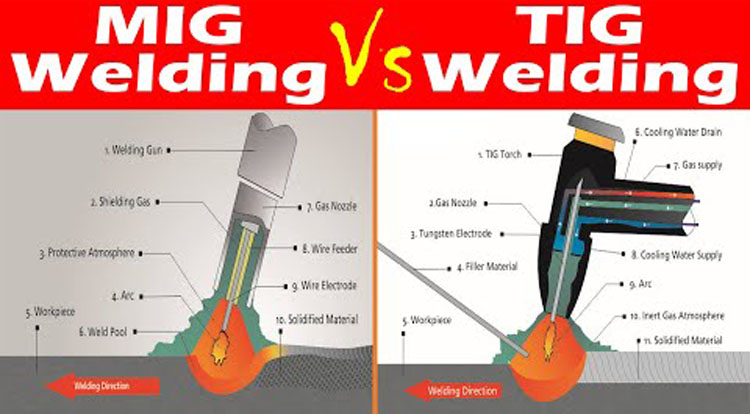
Photo by YT@AcademicGainTutorials
What is welder?
Welders also use butt welds and seam welds. Butt welds use a filler metal to create a joint between two pieces of metal. The filler metal fills in the space between the two pieces of metal. Seam welds use a special metal called a seam sealer to create a joint between two pieces of metal. Seam welds are stronger than butt welds because they don’t require a filler metal.
What are the main differences?
Mig Welder
A mig welder is a specialized machine that uses a high-frequency arc to weld metals. Unlike conventional welding machines, which use a lower-frequency arc to melt a pool of metal between two electrodes, a mig welder uses a high frequency of an arc to produce a weld. Mig welding is primary welding, which means the weld is produced by the metal-to-metal contact between the work pieces. Tig welding, on the other hand, is an advanced welding technique that uses Tig welding rods to weld different metals, including non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper or stainless steel.
MIG welding machines come in different sizes that are designed for industrial, structural, heavy-duty and automotive welding. These machines are mainly used in manufacturing industries and construction sites where high volumes of welding are necessary. Some companies use mig welding machines in their operations to produce custom-built parts, like metal-pipe welders, that are used in oil and gas production.
Tig Welder
A Tig welder is a welding machine that uses Tig welding rods to produce welds on different types of metals. Unlike mig welders, which produce welds by melting a pool of metal between two electrodes, tig welders use high-frequency welding to produce joinings between different metals. Tig welding is a specialized welding technique that produces welds by melting a pool of metal with a high-frequency welding arc.
Unlike mig welding, which produces a weld between two pieces of metal, a tig welder uses a high-frequency arc to weld different types of metals like aluminum, steel and stainless steel. Because tig welding relies more on electrical energy than welding chemicals, a tig welder can weld different materials like aluminum, steel and stainless steel.
This makes it a viable option for welding different materials, including aerospace parts and components that require high-strength welds.
Difference Between Mig Welder vs Tig Welder
Now that you know what a mig welder and a tig welder are, let’s look at the key differences between these two welding machines. – Power Source – Frequency of Welding Arc – Welding Area – Welder Equipment – Working of Mig Welders.
Mig welding machines use a high-frequency arc to produce welds. Some mig welders have a dual voltage option that uses either 110 or 220 volts for welding. Electrical power in welding machines is produced by a motor, which is connected to the work piece by a guide. As the work piece rotates, it moves through the welding arc.
When the work piece moves through the welding arc, the heat from the arc melts the metal in the work piece and the impact from the arc deposits the metal in the work piece. The welding area of a mig welder can be between 10 and 200mm. It is important to know that the welding area determines the thickness of the weld. A mig welder can produce welds with 3/32nd-inch, 1/8th-inch and 3/16th-inch thicknesses.
On the other hand, a tig welder uses high-frequency welding to weld different metals. Every tig welder is different and it can weld different metals depending on the electrode and shielding gas settings of the tig welder.
Working of Mig Welders
Mig welders produce welds by melting a pool of metal between two electrodes. They are primarily used for industrial welding and construction where high volumes of welding are required. Mig welders have a high-frequency welding arc with a fairly large welding area. The welding area of a mig welder is between 10 and 200mm. The larger the welding area of a mig welder, the thicker the weld it produces.
The welding process of a mig welder is similar to that of a stick welder. A high-frequency arc is used to break the metal down into a liquid pool of metal. Then, the work pieces are placed in the weld zone and moved through the welding arc.
Mig welders consist of a power unit, a welding unit, a weld-through-force gauge, a welding gun, a welding stand and a welding cable. The welding cable usually has a wire gauge of 20 to 28, depending on the mig welder model. The welding cable is usually plugged into the welding unit on the side of the welding machine.
Last But Not List about Mig Welder vs Tig Welder
Mig welding machines are best suited for welding thick metals like steel and aluminum. They produce thick welds and fill any gaps between material pieces. On the other hand, tig welders are mostly used for welding thinner metals like aluminum. They produce a weld that is only about 1/4-inch thick. So, if you are looking for a welding machine to weld thinner metals, a tig welder is the best choice for you.
