To calculate wire feed speed in MIG welding, multiply the desired current (amperage) by the wire feed speed constant. This constant varies based on wire diameter and material.
Wire feed speed (WFS) is critical in MIG welding for achieving optimal weld quality. It determines the rate at which the welding wire is fed into the weld pool, influencing penetration, bead shape, and weld strength. Proper WFS ensures consistent arc stability and efficient deposition rates.
Factors like wire diameter, material type, and welding position affect the ideal WFS. Understanding these elements helps welders set the correct parameters, leading to improved weld integrity and reduced defects. Mastering WFS calculation enhances productivity, minimizes waste, and ensures strong, reliable welds.
Introduction To Mig Welding
MIG welding is a popular welding technique. It stands for Metal Inert Gas welding. This method uses a continuous wire feed. The wire acts as an electrode and filler metal. MIG welding is known for its speed and versatility. It produces clean and strong welds.
Basics Of Mig Welding
In MIG welding, a welding gun feeds the wire. The wire melts to join metals together. The process uses an inert gas like argon. The gas shields the weld area from contamination. Key components include the welding gun, wire, and gas supply.
- Welding Gun: Holds the wire and gas nozzle.
- Wire: Acts as the electrode and filler material.
- Gas Supply: Protects the weld from impurities.
Importance Of Wire Feed Speed
Wire feed speed is crucial in MIG welding. It affects the quality of the weld. The speed is the rate at which the wire feeds through the gun. Adjusting this speed is vital for different materials and thicknesses. Correct speed ensures strong and smooth welds. Incorrect speed can cause problems.
| Wire Feed Speed | Effect on Weld |
|---|---|
| Too High | Excessive spatter and poor fusion |
| Too Low | Weak weld and poor penetration |
| Optimal | Strong, clean, and smooth weld |
To calculate wire feed speed, use the formula below:
Wire Feed Speed (inches per minute) = (Amps × 1.6) / Wire Diameter
Remember to adjust the speed based on the material and thickness. A consistent and correct wire feed speed ensures high-quality welds.

Credit: www.thewelderswarehouse.com
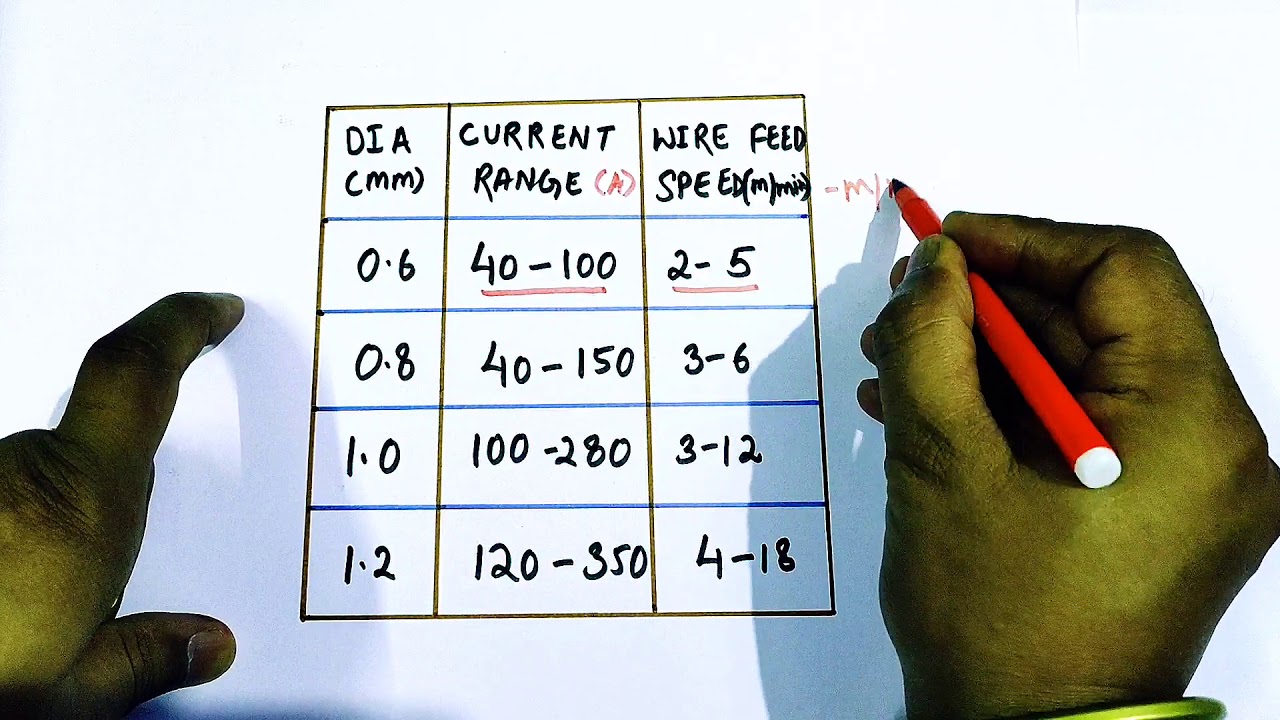
Factors Affecting Wire Feed Speed
Calculating wire feed speed in MIG welding is essential for quality welds. Several factors influence the wire feed speed, each playing a crucial role. Understanding these factors helps in achieving the best results. Below are some key factors affecting wire feed speed.
Material Type
The type of material being welded significantly impacts the wire feed speed. Different materials have unique properties requiring specific settings.
- Steel: Requires a moderate wire feed speed.
- Aluminum: Needs a higher wire feed speed due to its higher conductivity.
- Stainless Steel: Demands a slower wire feed speed for precision.
Always adjust the feed speed according to the material type. This ensures optimal penetration and minimal spatter.
Thickness Of Metal
The thickness of the metal determines the wire feed speed. Thicker metals need different settings compared to thinner ones.
| Metal Thickness | Recommended Wire Feed Speed |
|---|---|
| Thin (1/8 inch or less) | High speed |
| Medium (1/8 to 1/4 inch) | Moderate speed |
| Thick (over 1/4 inch) | Low speed |
Setting the correct wire feed speed based on metal thickness ensures strong welds. It also prevents burn-through or poor fusion.
Calculating Wire Feed Speed
Calculating wire feed speed in MIG welding is essential. It ensures a strong and clean weld. The correct speed affects the weld quality and the overall process efficiency. This guide will walk you through the necessary steps.
Required Tools And Equipment
- Wire feeder
- Welding machine
- Welding wire
- Calculator
- Measuring tape
Step-by-step Calculation
- Determine the wire diameter.
- Check the voltage setting on the welding machine.
- Refer to the manufacturer’s chart for wire feed speed.
- Measure the wire feed speed. Pull the trigger and let the wire feed for 10 seconds.
- Measure the wire length fed in 10 seconds.
- Multiply the measured length by 6. This gives the wire feed speed in inches per minute (IPM).
Wire feed speed calculation example:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Wire Diameter | 0.035 inches |
| Voltage Setting | 20 volts |
| Measured Length in 10 Seconds | 15 inches |
| Wire Feed Speed (IPM) | 15 x 6 = 90 IPM |
Ensure that all measurements are accurate. This helps in achieving the best results.

Credit: royalweldingwires.com
Optimal Wire Feed Speed Settings
Finding the optimal wire feed speed settings in MIG welding is crucial. This ensures strong, clean, and consistent welds. Proper settings vary based on the type and thickness of the metal. Adjusting these settings can make a significant difference in the quality of your work.
Settings For Different Metals
Different metals require different wire feed speed settings. Below are guidelines for common metals:
| Metal Type | Wire Feed Speed (inches per minute) |
|---|---|
| Mild Steel | 300 – 500 |
| Stainless Steel | 200 – 400 |
| Aluminum | 350 – 600 |
Adjust the wire feed speed based on the specific properties of each metal. Here are some tips for common metals:
- Mild Steel: Maintain moderate speeds for consistent welds.
- Stainless Steel: Use lower speeds to prevent burn-through.
- Aluminum: Higher speeds help avoid oxidation.
Adjusting For Thickness
The thickness of the metal also influences the wire feed speed. Use higher speeds for thicker metals to ensure deep penetration. Thinner metals require slower speeds to prevent warping or burn-through. Here is a simple guide:
| Metal Thickness | Wire Feed Speed (inches per minute) |
|---|---|
| 1/16 inch | 100 – 200 |
| 1/8 inch | 200 – 300 |
| 1/4 inch | 300 – 400 |
Follow these steps to adjust wire feed speed for thickness:
- Measure the metal thickness.
- Refer to the recommended speed range.
- Set the wire feed speed accordingly.
Correctly setting the wire feed speed ensures optimal weld quality. It reduces the risk of defects and enhances the strength of the weld.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Calculating the wire feed speed in MIG welding is crucial. Mistakes can lead to poor weld quality. Understanding common errors helps to avoid them.
Overfeeding And Underfeeding
Overfeeding the wire can cause excessive spatter and burn-back. This happens when the wire speed is too fast. The wire builds up in the weld pool. This leads to a messy and weak weld.
Underfeeding occurs when the wire speed is too slow. The arc becomes unstable. The weld may have insufficient penetration. This can lead to weak joints and poor quality welds.
Inconsistent Speed
Maintaining a consistent wire feed speed is essential. Inconsistent speed leads to irregular bead appearance and weak spots. It can cause porosity and cracks in the weld.
Ensure the wire feed mechanism is well-maintained. Check the drive rolls, liner, and contact tip. Clean and replace them as needed. This helps in maintaining a stable speed.
Use the correct settings on the welder. Adjust the speed based on the material and thickness. Practice and adjust until achieving a consistent feed.
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Overfeeding | Too fast wire speed | Reduce wire feed speed |
| Underfeeding | Too slow wire speed | Increase wire feed speed |
| Inconsistent Speed | Poor maintenance | Maintain and clean equipment |
Credit: www.youtube.com
Expert Tips For Beginners
Starting with MIG welding can be a bit overwhelming. Calculating the wire feed speed is crucial for a successful weld. Here are some expert tips to help beginners. These tips ensure precision and efficiency in your welding projects.
Practice And Patience
Practice is essential. Start with scrap metal pieces. Adjust the wire feed speed until you get a consistent weld. Patience is key. Do not rush the process. Take your time to understand the settings. Mistakes are part of learning. Keep practicing and you will improve.
Using Charts And Guides
Charts and guides are invaluable tools. They provide recommended settings for different materials and thicknesses. Use these charts to set the correct wire feed speed. Here is a simple example:
| Material Thickness (inches) | Wire Feed Speed (inches per minute) |
|---|---|
| 0.035 | 250-300 |
| 0.045 | 275-350 |
| 0.0625 | 300-375 |
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines. These guides ensure you stay within safe and effective ranges. They help avoid common mistakes and improve your welding quality.
Advanced Techniques
Mastering MIG welding involves more than basic techniques. Advanced methods can greatly enhance your weld quality. Learn how to fine-tune your wire feed speed with these advanced techniques.
Pulse Welding
Pulse welding is a sophisticated MIG welding technique. It offers better control over the heat input. This reduces the risk of burn-through and warping. The process involves alternating between high and low current. This creates “pulses” that allow for better penetration and a more stable arc.
To calculate wire feed speed in pulse welding, follow these steps:
- Determine the base current and peak current settings.
- Measure the pulse frequency and duration.
- Adjust the wire feed speed to match the pulse settings.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate the relationship:
| Setting | Base Current | Peak Current | Pulse Frequency | Wire Feed Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 | 100 A | 300 A | 50 Hz | 400 in/min |
| Example 2 | 150 A | 350 A | 60 Hz | 500 in/min |
Spray Transfer
Spray transfer is another advanced MIG welding technique. It involves a high current setting. This creates a spray of tiny molten droplets. These droplets transfer from the wire to the weld pool.
To adjust the wire feed speed for spray transfer:
- Set a high current, usually above 250 amps.
- Use a higher voltage setting.
- Increase the wire feed speed to keep up with the high current.
Here’s a quick reference:
- High current: above 250 amps
- High voltage: to support the current
- Wire feed speed: 500-700 in/min
These advanced techniques can significantly improve your MIG welding results. Adjusting the wire feed speed accurately is crucial. Practice these methods to achieve superior welds.
Maintenance And Troubleshooting
Maintaining and troubleshooting your MIG welding equipment is crucial. This ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of your tools. Regular checks and timely fixes help avoid unexpected breakdowns. Let’s explore how to keep your equipment in top shape.
Regular Equipment Checks
Regular equipment checks are essential. These checks help identify potential problems early.
- Inspect cables and connectors for wear and tear.
- Check the wire feed speed settings for accuracy.
- Ensure the contact tip is clean and free of debris.
- Look for any loose parts or fittings.
Perform these checks before each welding session. This helps maintain a smooth workflow.
Identifying And Fixing Issues
Identifying issues early can prevent major problems. Here are common issues and their fixes:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent wire feed | Dirty drive rolls | Clean or replace drive rolls |
| Burnback | Poor contact tip condition | Replace the contact tip |
| Poor arc stability | Incorrect wire feed speed | Adjust wire feed speed |
| Wire slipping | Loose tensioner | Tighten the tensioner |
Always address these issues promptly. This ensures your MIG welding process remains efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Wire Feed Speed In Mig Welding?
Wire feed speed is the rate at which the welding wire is fed into the weld. It’s measured in inches per minute (IPM) or millimeters per minute (MPM). The correct speed ensures a smooth and consistent weld.
How To Calculate Wire Feed Speed?
To calculate wire feed speed, multiply the desired current (amperage) by the wire feed speed constant. This constant varies with wire diameter. Check the welding wire specifications for accurate numbers.
Why Is Wire Feed Speed Important?
Wire feed speed is crucial for controlling weld penetration and bead appearance. Proper speed ensures a stable arc and quality welds. Incorrect speed can lead to defects like porosity or excessive spatter.
What Factors Affect Wire Feed Speed?
Several factors affect wire feed speed, including wire diameter, material type, and welding position. Adjusting these factors helps achieve optimal welding performance and quality.
Conclusion
Mastering wire feed speed in MIG welding enhances weld quality and efficiency. Practice and precise calculations ensure optimal results. Always consider material type and thickness for best outcomes. Stay updated with industry standards and continually refine your skills. Achieving proper wire feed speed leads to stronger, more reliable welds every time.
