Arc welding uses a consumable electrode, while TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. Both methods have specific uses and benefits.
Arc welding, also known as stick welding, is widely used for its versatility and ease of use. It is suitable for heavy-duty tasks and works well on rusty or dirty metals. TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, offers precision and control, making it ideal for thin materials and detailed work.
This method produces cleaner and stronger welds but requires more skill and time. Understanding the differences between these welding techniques helps in choosing the right one for your project, ensuring optimal results and efficiency. Both methods are essential in various industries and applications.
Credit: americantorchtip.com
Introduction To Welding Techniques
Welding is a key process in many industries. It joins materials together. Two common welding techniques are Arc welding and Tig welding. Each has unique features and benefits.
Importance Of Welding
Welding is crucial in construction, automotive, and manufacturing. It ensures the strength and durability of structures. Reliable welding techniques are essential for safety and quality.
Overview Of Arc And Tig Welding
Arc welding uses an electric arc to melt metals. It is versatile and commonly used. Tig welding uses a tungsten electrode and is known for precision. It is ideal for detailed work.
| Feature | Arc Welding | Tig Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Electric Arc | Tungsten Electrode |
| Materials | Various Metals | Mostly Thin Metals |
| Skill Level | Moderate | High |
| Applications | Construction, Repair | Automotive, Art |
Basics Of Arc Welding
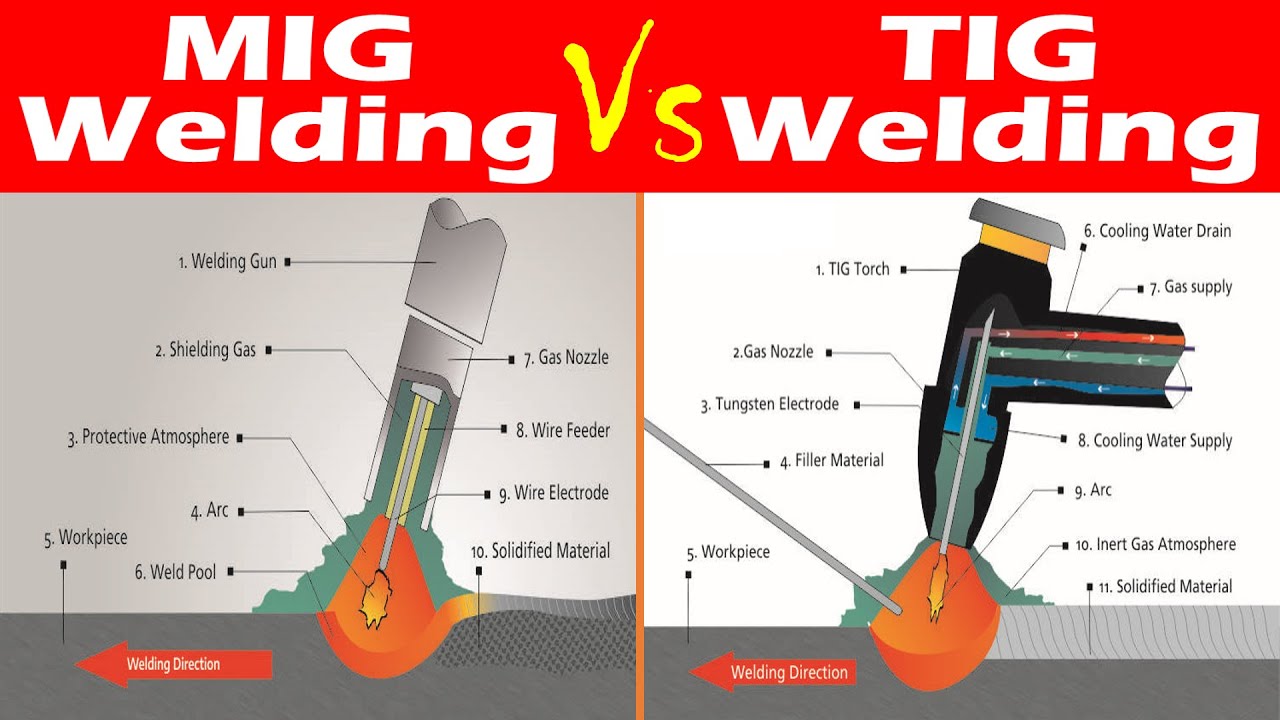
Arc welding is a type of welding that uses an electric arc to melt metals at the welding point. It is one of the most common welding techniques and is favored for its simplicity and versatility. Understanding the basics of arc welding is essential for anyone interested in welding.
How Arc Welding Works
The process of arc welding involves creating an electric arc between an electrode and the base material. This arc generates intense heat, which melts the metal. Once the metal cools, it forms a strong joint. The melted metal, known as the weld pool, cools and solidifies, binding the pieces together.
Here is how it works step-by-step:
- The welder connects the power supply to the electrode and the base material.
- The welder strikes an arc by bringing the electrode close to the base material.
- The electric arc generates heat, melting the base material and the electrode.
- The molten material forms a weld pool, which cools and solidifies.
Key Components
Arc welding involves several key components that ensure the welding process is efficient and effective.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Provides the necessary electrical energy for welding. |
| Electrode | Conducts the electrical current and melts to form the weld. |
| Base Material | The metal pieces that are being joined together. |
| Welding Machine | Controls the electrical parameters and supports the welding process. |
Besides these, welders use protective gear to ensure safety during the welding process.
- Welding Helmet
- Gloves
- Protective Clothing
Understanding these components is crucial for successful welding.
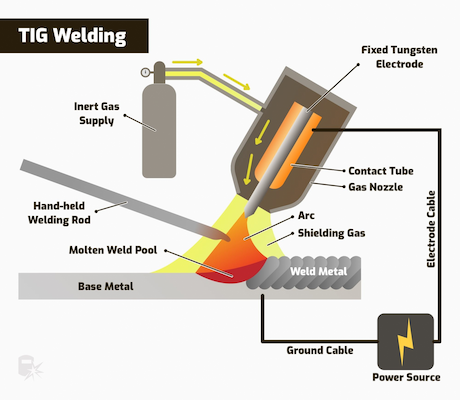
Basics Of Tig Welding
Tig Welding, also known as Tungsten Inert Gas welding, is a precise welding method. It uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. This technique is ideal for projects requiring strong, high-quality welds. It works well on thin materials and allows for intricate designs.
How Tig Welding Works
Tig Welding operates by creating an arc between a tungsten electrode and the workpiece. A shielding gas, usually argon, protects the weld area from contamination. The welder manually feeds a filler rod into the weld pool, if needed. This method requires skill and practice but offers excellent control.
Key Components
The key components of Tig Welding include:
- Tungsten Electrode: Non-consumable, conducts the welding current.
- Shielding Gas: Protects the weld area, commonly argon or helium.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary current for welding.
- Filler Rod: Adds material to the weld, used for thicker joints.
- Foot Pedal: Controls the welding current, offering precision.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Tungsten Electrode | Conducts the welding current. |
| Shielding Gas | Protects the weld area from contamination. |
| Power Supply | Provides the current for the welding process. |
| Filler Rod | Adds material to the weld joint. |
| Foot Pedal | Controls the welding current for precision. |

Credit: customfabricators.net
Comparing Arc And Tig Welding
Choosing the right welding method is crucial for any project. Arc welding and TIG welding are two popular techniques. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, and they are used for different applications. This comparison will help you understand which method suits your needs better.
Strengths And Weaknesses
Arc welding is known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. It requires less equipment, making it ideal for beginners. Here are the strengths and weaknesses of arc welding:
- Strengths:
- Easy to learn and use
- Lower equipment costs
- Works well on thicker materials
- Suitable for outdoor use
- Weaknesses:
- Produces more spatter
- Less precise than TIG welding
- Not ideal for thin materials
- Requires post-weld cleaning
TIG welding offers high precision and quality. It is best for detailed work. Here are the strengths and weaknesses of TIG welding:
- Strengths:
- High precision and control
- Produces clean welds with minimal spatter
- Best for thin materials
- Works well with various metals
- Weaknesses:
- Requires more skill and training
- Higher equipment costs
- Slower process
- Not ideal for outdoor use
Applications And Uses
Arc welding is versatile and widely used. Here are some common applications:
- Construction and building repairs
- Heavy machinery and equipment repair
- Shipbuilding
- Pipeline welding
TIG welding is preferred for intricate and delicate projects. Here are some typical uses:
- Automotive and aerospace industries
- Art and sculpture
- Custom metal fabrication
- Medical device manufacturing
Understanding the strengths, weaknesses, and applications of each method helps in making an informed choice. Each welding type has its own niche where it excels.
Materials And Suitability
Choosing between Arc Welding and Tig Welding depends on the materials. Each technique has its strengths. Understanding these will help you make the best choice.
Types Of Materials
Arc Welding and Tig Welding work with different materials. Here are the common materials for each:
| Technique | Materials |
|---|---|
| Arc Welding |
|
| Tig Welding |
|
Choosing The Right Technique
Consider the material’s properties when picking a welding technique. Here’s a guide:
- Arc Welding: Ideal for thicker materials. It handles rough surfaces well.
- Tig Welding: Best for thin and delicate materials. It offers precise control.
Use Arc Welding for heavy-duty projects. It works well with construction and repair. Tig Welding suits projects needing clean, high-quality welds. It’s perfect for automotive and aerospace industries.
Skill Level And Training
Arc Welding and Tig Welding require different skill levels and training. Understanding these differences helps beginners choose the right path. This section covers the learning curve and training resources for both methods.
Learning Curve
The learning curve for Arc Welding is moderate. It is suitable for beginners. Basic skills can be acquired in a few weeks. This method uses a simpler setup and fewer controls.
Tig Welding has a steeper learning curve. It is more complex and requires precision. This method demands steady hands and good coordination. Mastery takes longer and involves more practice.
Training Resources
There are various training resources for both welding methods:
- Arc Welding:
- Online tutorials and videos
- Community college courses
- On-the-job training
- Tig Welding:
- Advanced online courses
- Trade school programs
- Certification programs
Below is a table summarizing the training resources:
| Training Resource | Arc Welding | Tig Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Online Tutorials | ✔ | ✔ |
| Community College | ✔ | ✔ |
| Trade School | ✘ | ✔ |
| On-the-job Training | ✔ | ✘ |
| Certification Programs | ✘ | ✔ |
Choosing the right training resource depends on your goals. Beginners may start with online tutorials. Advanced learners benefit from trade schools and certifications.
Cost Considerations
When comparing arc welding and TIG welding, cost considerations play a crucial role. Different factors, like equipment and operational costs, impact your choice. This section explores these aspects, helping you make an informed decision.
Equipment Costs
The initial investment for arc welding equipment is generally lower. Arc welders are often more affordable and widely available. On the other hand, TIG welding equipment tends to be more expensive.
Here is a simple comparison:
| Equipment | Arc Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Welder Cost | $200 – $800 | $1,000 – $3,000 |
| Accessories | $50 – $200 | $100 – $400 |
These costs can vary based on brand and model. Yet, TIG welding equipment consistently remains pricier.
Operational Costs
Operational costs also differ significantly between the two welding methods. Arc welding uses consumable electrodes, which can add up over time. TIG welding, however, uses non-consumable tungsten electrodes.
Other operational cost considerations include:
- Power consumption: Arc welding usually consumes more power.
- Shielding gas: TIG welding often requires a continuous supply of argon gas.
- Maintenance: TIG welding equipment may need more upkeep.
Here’s a breakdown:
| Operational Cost | Arc Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Electrodes | $50/month | $20/month |
| Shielding Gas | Not Required | $30/month |
| Power Usage | Higher | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Higher |
While arc welding equipment is cheaper, TIG welding can offer savings in operational costs. Weighing these factors can guide you towards the most cost-effective choice for your needs.
Safety Measures
Understanding Safety Measures is crucial for both Arc Welding and Tig Welding. Each technique involves risks that require specific precautions. This section outlines essential safety steps to keep welders safe.
Protective Gear
Welders must wear proper protective gear to avoid injuries. Here’s a list of essential items:
- Welding Helmet with auto-darkening feature
- Fire-Resistant Jacket
- Welding Gloves
- Safety Glasses
- Respirator for fumes
- Leather Apron
- Steel-Toed Boots
Safety Tips
Follow these safety tips to minimize the risks associated with welding:
- Ensure the work area is well-ventilated.
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
- Never weld in wet or damp conditions.
- Inspect equipment before use for any damages.
- Maintain a clean workspace to avoid tripping hazards.
- Use clamps to secure materials during welding.
- Always turn off equipment when not in use.
Adhering to these safety measures ensures a safer welding environment for everyone involved.
Environmental Impact
Understanding the environmental impact of welding methods is crucial. Both arc welding and TIG welding have unique effects on our environment. Let’s explore these impacts in detail.
Emissions And Waste
Arc welding produces more emissions compared to TIG welding. The process generates significant amounts of fumes and gases. Some of these emissions are harmful and can affect air quality.
TIG welding, on the other hand, produces fewer emissions. This method uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode, reducing the generation of waste. Less harmful fumes are released into the air, making it a cleaner option.
| Welding Method | Emissions | Waste |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Welding | High | Significant |
| TIG Welding | Low | Minimal |
Sustainability
Sustainability is a key factor in modern manufacturing. TIG welding is known for its energy efficiency. It uses less power and produces long-lasting joints. This reduces the need for frequent repairs.
Arc welding, though effective, consumes more energy. This high energy consumption results in a larger carbon footprint. The materials used in arc welding often produce more waste, affecting overall sustainability.
Switching to TIG welding can enhance a company’s eco-friendliness. It supports sustainable practices and helps in reducing environmental damage.
- Energy Efficiency: TIG welding is more efficient.
- Material Usage: Arc welding uses more materials.
- Eco-Friendliness: TIG welding is better for the environment.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Arc Welding?
Arc welding is a process that uses an electric arc to join metals. The heat from the arc melts the metal, allowing for fusion.
What Materials Can Tig Welding Join?
TIG welding can join a wide range of metals. This includes stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. It’s suitable for thin materials.
Which Welding Method Is More Precise?
TIG welding is more precise than arc welding. It allows for better control and produces cleaner welds.
Is Tig Welding More Difficult Than Arc Welding?
Yes, TIG welding is generally more difficult. It requires more skill and control compared to arc welding.
Conclusion
Choosing between arc welding and TIG welding depends on your project needs. Arc welding is faster and more economical. TIG welding offers precision for delicate tasks. Evaluate your requirements and skill level. Both methods have unique benefits. Select the one that best suits your specific welding applications for optimal results.
