Fusion welding is a process that joins materials by melting and fusing them together. It uses heat to create a strong bond.
Fusion welding is a critical technique in many industries. It involves heating materials until they reach their melting point. Once melted, the materials merge to form a seamless joint. This method is essential for creating durable and robust connections. Fusion welding is commonly used in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries.
It offers high precision and strong, long-lasting bonds. The process can be automated, making it efficient for large-scale projects. Safety measures are crucial due to the high temperatures involved. Mastery of fusion welding can lead to career advancement in various technical fields. This technique is fundamental for modern manufacturing and construction.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Introduction To Fusion Welding
Fusion welding is a key process in joining metals. It involves melting and fusing materials together. This method creates strong and durable joints. Fusion welding is essential in many industries.
Basics Of Fusion Welding
Fusion welding melts two pieces of metal. The melted parts mix and cool down. This forms a single piece. Different techniques achieve this. Common methods include:
- Arc Welding: Uses an electric arc to melt metals.
- Gas Welding: Uses a gas flame for melting.
- Laser Welding: Uses a laser beam for precision.
Each method has its own tools and settings. They all aim to create a strong joint.
Importance In Manufacturing
Fusion welding is crucial in manufacturing. It joins parts to make products. Many industries rely on it. These include:
- Automotive: For car bodies and frames.
- Aerospace: For aircraft structures.
- Construction: For building frameworks.
- Shipbuilding: For hulls and decks.
Fusion welding ensures the strength and safety of products. It also helps in mass production. This makes it vital for modern manufacturing.
Types Of Fusion Welding
Fusion welding is a process that joins materials by melting them together. There are various types of fusion welding methods, each with unique advantages. Understanding these types helps choose the right method for specific applications.
Arc Welding
Arc welding uses an electric arc to melt materials. This method is versatile and widely used.
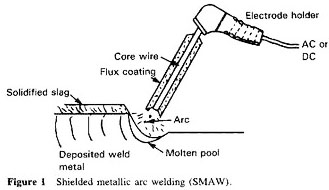
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Uses a consumable electrode.
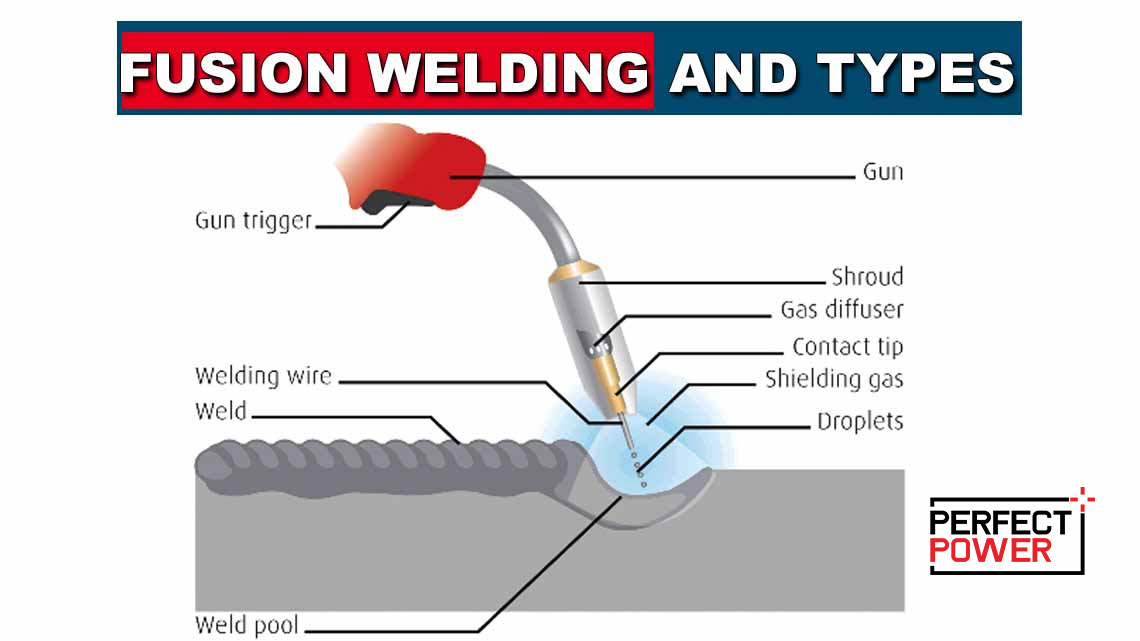
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW): Uses a continuous wire feed.
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW): Uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode.
Arc welding is effective for various metals and thicknesses. It offers high strength and durability.
Gas Welding
Gas welding involves using a flame to melt materials. It is often used for thinner materials.
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding: Uses oxygen and acetylene gas.
- Oxy-Hydrogen Welding: Uses oxygen and hydrogen gas.
Gas welding is portable and easy to control. It is ideal for small repairs and precise work.
Laser Welding
Laser welding uses a laser beam to melt materials. It offers high precision and speed.
- Continuous Wave Laser Welding: Provides constant laser output.
- Pulsed Laser Welding: Delivers laser in short bursts.
Laser welding is suitable for delicate and high-precision tasks. It is used in industries like aerospace and electronics.
| Type | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Welding | High strength, versatile | Construction, manufacturing |
| Gas Welding | Portable, easy to control | Small repairs, thin materials |
| Laser Welding | High precision, fast | Aerospace, electronics |
Fusion Welding Techniques
Fusion welding is a process that joins materials by melting them. This technique is used in various industries to create strong, durable bonds. There are two primary categories of fusion welding techniques: manual and automated. Each method has its own applications and advantages.
Manual Techniques
Manual fusion welding techniques require a skilled operator. The welder controls the welding process by hand, ensuring precision. Here are some common manual techniques:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Also known as stick welding, it uses an electrode coated in flux to lay the weld.
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW): Also called TIG welding, it uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. This technique provides high-quality welds.
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW): Known as MIG welding, it uses a continuous wire feed as an electrode. This method is fast and efficient.
Automated Techniques
Automated fusion welding techniques use machines to perform the welding process. This reduces human error and increases production speed. Here are some common automated techniques:
- Robotic Welding: Robots perform the welding process with high precision. This technique is ideal for repetitive tasks.
- Laser Beam Welding (LBW): Uses a high-intensity laser to join materials. It provides deep welds and minimal distortion.
- Electron Beam Welding (EBW): Uses a beam of high-velocity electrons. This technique is excellent for thick materials.
Manual and automated techniques each have their own benefits. Manual techniques offer flexibility and control, while automated techniques provide speed and consistency. Choosing the right method depends on the specific needs of the project.
Materials And Fusion Welding
Fusion welding is a popular method in the welding industry. It involves melting base materials to join them together. Understanding the materials used in fusion welding is crucial for successful results. Different materials behave differently under heat and pressure.
Common Materials Used
Various materials are suitable for fusion welding. Here are some common ones:
- Steel: Often used in construction and manufacturing.
- Aluminum: Popular in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Copper: Common in electrical applications.
- Nickel: Used for high-temperature applications.
- Magnesium: Lightweight, used in automotive parts.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are compatible with fusion welding. Compatibility depends on several factors:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | Materials must have similar melting points. |
| Thermal Conductivity | High conductivity materials require more heat. |
| Oxidation | Some materials oxidize quickly when heated. |
| Expansion | Materials expand differently under heat. |
Proper selection ensures strong, durable welds. Always consult material specifications before welding.
Equipment For Fusion Welding
Fusion welding is an advanced technique that joins materials by melting them together. A variety of equipment is used to ensure high-quality welds. This section will discuss the essential tools and advanced machinery needed for fusion welding.
Essential Tools
Fusion welding requires several essential tools to achieve precision and quality. Below is a table summarizing the key tools you need:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Welding Torch | Heats and melts the materials |
| Protective Gear | Ensures safety during welding |
| Welding Rods | Adds filler material |
| Wire Brush | Cleans welded area |
Using these tools properly ensures a strong and durable weld. A welding torch is crucial for heating and melting materials. Protective gear like gloves and goggles keeps you safe. Welding rods add filler material to the weld. A wire brush helps clean the welded area.
Advanced Machinery
Advanced machinery enhances the efficiency and quality of fusion welding. Here are some of the advanced machines commonly used:
- Welding Robots: Automate the welding process
- Welding Positioners: Hold and rotate workpieces
- Plasma Cutters: Cut through metal with precision
- Fume Extractors: Remove harmful fumes
Welding robots automate the welding process, increasing speed and precision. Welding positioners hold and rotate workpieces, making it easier to weld complex shapes. Plasma cutters allow precise cutting of metal, while fume extractors remove harmful fumes, ensuring a safer work environment.
Using both essential tools and advanced machinery results in high-quality fusion welds. Equip your workshop with these tools to achieve the best results.
Safety In Fusion Welding
Fusion welding involves joining materials using intense heat. Safety is crucial during this process. Proper safety measures prevent injuries and accidents. This section covers essential safety aspects in fusion welding.
Protective Gear
Wearing the right protective gear is vital. Welders need to protect their eyes, skin, and lungs. Here are key protective items:
- Welding Helmet: Shields eyes and face from sparks and UV radiation.
- Welding Gloves: Protect hands from heat and burns.
- Protective Clothing: Wear flame-resistant clothing to guard against sparks.
- Respirator: Prevents inhalation of harmful fumes and gases.
- Safety Boots: Steel-toed boots protect feet from heavy objects and heat.
Safety Procedures
Following safety procedures minimizes risks. Here are essential safety steps:
- Inspect Equipment: Check all tools and machines before use.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation to remove fumes.
- Fire Safety: Keep fire extinguishers nearby.
- Training: Only trained personnel should perform welding tasks.
- Emergency Plan: Know the emergency procedures and exits.
Safety in fusion welding is paramount. Using the right gear and following procedures keeps everyone safe.
Applications Of Fusion Welding
Fusion welding is a versatile technique. It joins materials by melting them together. This process has widespread applications across various industries. Below are some key sectors where fusion welding plays a crucial role.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry heavily relies on fusion welding. It ensures strong, durable joints in vehicle frames. Car manufacturers use it to weld body parts and engine components. This technique helps in creating lightweight yet robust vehicles. It also contributes to the safety and efficiency of automobiles.
Construction
In the construction industry, fusion welding is essential. It connects steel beams and structural components. This technique provides the strength needed for skyscrapers and bridges. Welders use it to assemble pipelines and reinforce concrete structures. Fusion welding ensures stability and longevity in construction projects.
Aerospace
The aerospace sector benefits immensely from fusion welding. Aircraft and spacecraft require precise and strong joints. Fusion welding is used to weld aircraft frames and rocket components. This technique ensures the integrity and safety of aerospace vehicles. It also supports the creation of lighter and more fuel-efficient aircraft.
Credit: hedhme.com
Challenges In Fusion Welding
Fusion welding is a popular process in various industries. It involves melting materials to join them together. Despite its benefits, there are several challenges that welders face. These challenges can affect the quality and efficiency of the weld. Understanding these issues can help in finding effective solutions.
Common Issues
Fusion welding comes with several common issues. Below are some of them:
- Porosity: Small holes can form inside the weld. These holes weaken the weld.
- Cracking: The weld can crack during cooling. This reduces the strength of the weld.
- Distortion: Heat can cause the metal to change shape. This can lead to misalignment.
- Inclusions: Foreign materials can get trapped in the weld. This affects the weld quality.
Solutions And Best Practices
To overcome these challenges, there are several solutions and best practices:
- Control Heat Input: Use appropriate heat settings to avoid excessive melting.
- Proper Cleaning: Clean the materials before welding. This prevents contamination.
- Use Filler Material: Use compatible filler materials to avoid cracking.
- Preheat and Post-Heat: Heat materials before and after welding. This reduces stress and cracking.
Below is a table summarizing common issues and their solutions:
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Porosity | Control Heat Input, Proper Cleaning |
| Cracking | Use Filler Material, Preheat and Post-Heat |
| Distortion | Control Heat Input |
| Inclusions | Proper Cleaning |
Future Of Fusion Welding
The future of fusion welding looks very exciting. Advances in technology and changing industry trends are shaping its path. This section dives into these changes.
Technological Advancements
Robotics and automation are transforming fusion welding. Robots can perform precise welds faster than humans. This improves efficiency and consistency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also playing a role. AI-powered systems can predict issues before they occur. This leads to fewer errors and higher-quality welds.
Laser welding is another major advancement. Lasers provide high precision and control. They are ideal for delicate or complex welding tasks.
Industry Trends
The demand for lightweight materials is growing. Industries like aerospace and automotive are using more aluminum and titanium. Fusion welding techniques are adapting to these materials.
Sustainability is becoming more important. Eco-friendly welding methods are being developed. These methods reduce waste and energy consumption.
Workforce training is also evolving. Virtual reality (VR) training programs are emerging. They offer safe and effective ways to train new welders.
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Robotics and Automation | Increased efficiency and precision |
| AI Systems | Higher quality welds, fewer errors |
| Laser Welding | Ideal for delicate tasks |
| Lightweight Materials | Adaptation of new techniques |
| Sustainability | Reduced waste and energy use |
| VR Training | Safe and effective training |
Credit: www.perfectwelders.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Fusion Welding?
Fusion welding is a process that joins materials by melting them. It creates a strong, continuous joint. It’s commonly used in metalworking and construction.
How Does Fusion Welding Work?
Fusion welding works by melting the base materials and adding filler. This forms a strong bond upon cooling. The process requires precise control of temperature and technique.
What Are Types Of Fusion Welding?
Types of fusion welding include arc welding, MIG welding, and TIG welding. Each method has specific applications and benefits. They are chosen based on the materials and project requirements.
Is Fusion Welding Safe?
Fusion welding can be safe with proper precautions. Use protective gear, maintain equipment, and follow safety guidelines. Training is essential to minimize risks and ensure safety.
Conclusion
Fusion welding is a vital process in various industries, offering strong and durable bonds. Understanding its methods and benefits can enhance your welding projects. Embrace the techniques and safety measures to achieve optimal results. Stay updated with new advancements to maintain a competitive edge in the welding field.
