Welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires careful consideration of filler materials and techniques to prevent corrosion and cracking. Use appropriate welding methods to ensure strong, durable joints.
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel is a common practice in various industries. It combines the strength of carbon steel with the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Proper filler materials, such as austenitic stainless steel electrodes, are essential for successful welding.
The welding process must carefully control heat input to minimize thermal expansion differences. Pre-weld and post-weld treatments can help reduce stress and prevent intergranular corrosion. This ensures a reliable and long-lasting weld. Proper preparation, including cleaning and aligning the materials, is crucial for achieving the best results. Using the right techniques and materials can produce high-quality, durable welds that meet industry standards.
Introduction To Welding Carbon Steel To Stainless Steel
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires special skills and techniques. This process is crucial in various industries. Understanding these techniques ensures strong and reliable welds.
Importance Of Proper Techniques
Using the correct techniques prevents issues like corrosion and cracking. Proper techniques ensure the weld area is durable and lasts longer. Different metals have different properties. Carbon steel and stainless steel expand and contract differently. This makes proper technique essential.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| TIG Welding | Provides precise control and clean welds. |
| MIG Welding | Great for thicker materials and fast welds. |
Common Applications
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel is common in many industries. Automotive and construction use this technique frequently. It is also used in oil and gas pipelines.
- Automotive parts and frames
- Construction beams and supports
- Oil and gas pipelines
- Food processing equipment
Each application requires specific considerations. Automotive parts need strong, lightweight welds. Construction beams require high-strength welds. Oil and gas pipelines must be corrosion-resistant. Food processing equipment requires sanitary welds. Each use case highlights the importance of proper techniques.

Credit: swantonweld.com
Understanding Material Differences
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires a solid understanding of their unique properties. Knowing the differences helps to achieve strong and durable welds. Each material has specific characteristics that influence the welding process.
Carbon Steel Properties
Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability. It mainly consists of iron and carbon. The carbon content typically ranges between 0.05% to 2.0%. Higher carbon content increases hardness but decreases ductility.
Some key properties of carbon steel include:
- High tensile strength
- Good malleability
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Cost-effective
- Prone to rusting
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High |
| Malleability | Good |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent |
| Cost | Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Poor |
Stainless Steel Properties
Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance. It contains iron, carbon, and at least 10.5% chromium. The chromium forms a protective layer on the surface, preventing rust.
Some key properties of stainless steel include:
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- High tensile strength
- Good ductility
- Resistant to high temperatures
- Higher cost
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | High |
| Ductility | Good |
| Temperature Resistance | High |
| Cost | High |
Challenges In Welding Dissimilar Metals
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel presents unique challenges. These metals have different properties. Careful planning and execution are essential.
Thermal Expansion Issues
Carbon steel and stainless steel expand at different rates. This causes stress during welding. If not managed, it can lead to cracks.
Thermal expansion differences can warp the metals. This affects the weld quality. It is crucial to control the heat input.
Using proper welding techniques can minimize these issues. Preheating the carbon steel helps balance the thermal expansion.
Corrosion Concerns
Welding dissimilar metals can lead to corrosion. Carbon steel is prone to rust. Stainless steel resists rust.
Mixing these metals can create galvanic corrosion. This happens when two different metals touch in a corrosive environment.
Use a suitable filler material to reduce corrosion risk. This helps create a stable joint between the metals.
Keep the weld area clean and free from contaminants. This also helps prevent corrosion.
Preparation Steps
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires careful preparation. Proper steps ensure a strong and durable joint. Below, we cover the essential preparation steps for achieving the best results.
Cleaning The Metals
Cleanliness is crucial for successful welding. Both carbon steel and stainless steel must be free from contaminants.
- Use a wire brush or grinder to remove surface rust, dirt, and grease.
- Apply a solvent like acetone to remove oils and residues.
- Ensure the cleaned surfaces are dry before welding.
Avoid cross-contamination. Use separate tools for each metal type. This prevents mixing impurities, which can weaken the weld.
Selecting The Right Filler Material
Choosing the appropriate filler material is vital for a strong weld.
| Type of Joint | Recommended Filler Material |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel to Stainless Steel | ER309L or ER309LSi |
| Thin Sections | ER308L |
Use ER309L or ER309LSi for most joints. For thin sections, ER308L works well. These fillers prevent cracking and corrosion in the weld area.
Choosing The Right Welding Method
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel can be a challenging task. Picking the right welding method is crucial for achieving strong, durable joints. Different welding techniques offer varying degrees of precision and strength. Below, we explore two popular welding methods: MIG and TIG welding.
Mig Welding
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), uses a continuous wire feed. It’s ideal for welding carbon steel to stainless steel due to its speed and efficiency.
- Speed: MIG welding is faster than many other methods.
- Ease of Use: It’s easier to learn and operate.
- Versatility: Suitable for various metal thicknesses.
MIG welding requires an inert gas to shield the weld area. Argon is commonly used for this purpose. The process also involves using a filler metal, ensuring a strong bond between the materials.
Tig Welding
TIG welding, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), offers precise control. It’s perfect for welding carbon steel to stainless steel, providing clean, high-quality welds.
- Precision: TIG welding allows for exact control over the weld.
- Quality: Produces high-quality, clean welds.
- Flexibility: Suitable for thin and thick materials alike.
In TIG welding, a non-consumable tungsten electrode generates the arc. A filler rod is used separately, which provides additional control over the welding process. Argon or helium gas is used to shield the weld area from contamination.
| Aspect | MIG Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast | Moderate |
| Precision | Good | Excellent |
| Ease of Use | Easy | Challenging |
Choosing between MIG and TIG welding depends on your specific needs. Consider the project requirements, material thickness, and desired weld quality to make an informed decision.
Welding Techniques
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires specific techniques to ensure a strong bond. The differences in the metals’ properties mean welders must take extra care. Below are some essential methods to achieve a successful weld.
Controlling Heat Input
Heat input is crucial when welding these different metals. Carbon steel and stainless steel respond differently to heat. Too much heat can cause warping and weaken the weld.
To manage heat input:
- Use a low heat input to avoid excessive melting.
- Employ pulse welding techniques for better control.
- Use shorter weld runs to minimize heat build-up.
Managing heat ensures both metals do not become compromised. The goal is to maintain the integrity of the weld.
Managing Weld Pool
The weld pool is the molten metal formed during welding. Proper management of the weld pool ensures a strong bond between carbon steel and stainless steel.
Key strategies include:
- Maintain a consistent weld pool size to ensure uniformity.
- Use filler metals compatible with both steel types.
- Monitor the weld pool temperature to prevent overheating.
A well-managed weld pool leads to a robust and reliable weld. It reduces the risk of defects and enhances the weld’s strength.
Post-welding Treatments
Post-welding treatments are essential for ensuring the durability and integrity of welded joints, especially when welding carbon steel to stainless steel. These treatments help to relieve stress, enhance surface finish, and improve overall performance.
Stress Relieving
Welding different metals, like carbon steel and stainless steel, creates residual stresses. These stresses can lead to cracks and distortions. Stress relieving is a heat treatment process that reduces these residual stresses. The welded piece is heated to a specific temperature and held there for a time.
Here is a simple table showing typical stress relieving temperatures:
| Material | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 540-650 |
| Stainless Steel | 480-900 |
After heating, the material is slowly cooled. This process helps to reduce the likelihood of cracks and ensures a stronger weld.
Surface Finishing
Surface finishing is crucial after welding carbon steel to stainless steel. It removes oxidation, weld spatter, and other impurities. This step ensures a clean and smooth surface.
Surface finishing techniques include:
- Grinding
- Polishing
- Pickling
- Passivation
Grinding and polishing smooth the welded joint, while pickling and passivation improve corrosion resistance. These processes enhance the appearance and longevity of the welded joint.
Ensuring proper post-welding treatments guarantees that the welded joint will perform reliably in various applications.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Safety Precautions
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires strict safety precautions. This ensures the safety of the welder and the quality of the weld. Below are the essential safety measures every welder should follow.
Personal Protective Equipment
Always wear the right Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) when welding.
- Welding Helmet: Protects your eyes and face from sparks and UV rays.
- Welding Gloves: Shields your hands from extreme heat and burns.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing: Prevents burns from sparks and hot metal.
- Safety Boots: Keeps your feet safe from falling objects and hot debris.
- Ear Protection: Guards against loud noises and potential ear damage.
Ventilation And Fume Control
Proper ventilation is crucial in welding. It helps to control fumes and gases.
- Use an exhaust hood to remove fumes directly from the source.
- Install local exhaust ventilation systems for better fume control.
- Ensure the workspace has adequate airflow.
- Wear a respirator if ventilation is insufficient.
Fumes from welding stainless steel contain chromium and nickel. These can be harmful if inhaled. Always prioritize safety and follow these precautions.
Expert Tips For Best Results
Welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires skill and precision. Achieving the best results demands attention to detail and adherence to specific techniques. Follow these expert tips to ensure success and avoid common pitfalls.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Use the Right Filler Material: Choose a compatible filler material to prevent corrosion and cracking.
- Control Heat Input: Excessive heat can lead to warping and weaken the weld.
- Clean the Surfaces: Remove any rust, oil, and contaminants before welding.
- Match the Welding Process: Select the appropriate welding process for the materials.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
Ensuring the structural integrity of your weld is crucial for safety and durability. Follow these steps:
- Preheat Carbon Steel: Preheating helps to reduce thermal stress and prevents cracking.
- Use Proper Welding Technique: Maintain a steady hand and consistent speed.
- Cool Down Gradually: Allow the weld to cool down slowly to prevent brittleness.
- Inspect the Weld: Perform a thorough inspection to check for defects and imperfections.
Table Of Recommended Welding Parameters
| Parameter | Carbon Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Filler Material | ER309 | ER309 |
| Preheat Temperature | 150-200°C | Not required |
| Cooling Rate | Slow | Moderate |
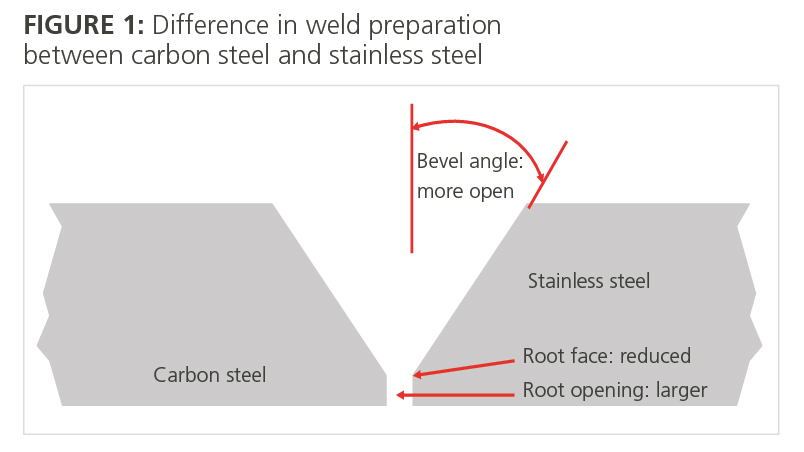
Credit: www.assda.asn.au
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Weld Carbon Steel To Stainless Steel?
Yes, you can weld carbon steel to stainless steel. Use a filler metal that is compatible with both metals. Proper preparation and technique are essential.
What Is The Best Welding Method For Carbon To Stainless Steel?
TIG welding is considered the best method. It offers precision and control, reducing the risk of contamination. MIG welding can also be used.
What Challenges Exist In Welding Carbon Steel To Stainless Steel?
The main challenges include different thermal expansion rates and potential galvanic corrosion. Proper technique and filler material choice are crucial.
Do You Need Special Filler Metals?
Yes, you need special filler metals. Use a high-nickel filler metal to ensure compatibility and strength between the two metals.
Conclusion
Successfully welding carbon steel to stainless steel requires knowledge, skill, and the right materials. Ensure proper preparation and technique for strong, durable welds. Follow these guidelines to achieve high-quality results and prevent issues. Mastering this process can greatly enhance your welding projects and open up new possibilities in metal fabrication.
