For TIG welding aluminum, pure argon gas is recommended. Argon provides a stable arc and excellent weld quality.
TIG welding aluminum requires a shielding gas to protect the weld area from contamination. Pure argon is the most commonly used gas for this purpose due to its ability to create a stable arc and produce clean, high-quality welds. Argon is an inert gas, meaning it does not react with the molten aluminum, ensuring a smooth and defect-free weld.
Using pure argon also helps in maintaining the structural integrity and strength of the aluminum. It is crucial to choose the correct gas to achieve optimal results in TIG welding aluminum.
Introduction To Tig Welding Aluminum
Tig welding aluminum is a precise and clean process. Many welders prefer this method for aluminum due to its superior control. Tig welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. It creates a high-quality weld that is strong and visually appealing.
Why Choose Tig Welding?
Tig welding offers excellent control over the welding process. This method allows for precise welds on thin materials. The welder can easily adjust the heat input, making it ideal for delicate aluminum parts. Tig welding also produces less spatter compared to other methods.
Benefits Of Tig Welding For Aluminum
- High-Quality Welds: Tig welding produces strong and clean welds.
- Precision: This method allows for detailed work on small parts.
- Less Distortion: The heat input is easily controlled, reducing the risk of warping.
- Versatility: Tig welding can be used on thin and thick aluminum materials.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Control | Allows precise adjustments |
| Quality | Produces clean and strong welds |
| Flexibility | Suitable for various aluminum thicknesses |
| Spatter | Minimal compared to other methods |
Essential Equipment
Aluminum welding requires precision and the right tools. Tig welding is the best method for aluminum. Here’s what you need for the job.
Tig Welder Setup
Setting up your Tig welder is crucial. Start by selecting a welder designed for aluminum. Ensure it has AC (alternating current) capabilities. AC helps clean the oxide layer on aluminum.
Next, set the amperage. Aluminum requires high amperage. For thin materials, use 60-80 amps. For thicker materials, increase to 150-200 amps. Use a foot pedal for precise control. This allows you to adjust the heat while welding.
Gas is essential for Tig welding aluminum. Argon is the best choice. It provides a stable arc. Ensure your gas flow rate is 15-20 cubic feet per hour (CFH).
Choosing The Right Torch
The right torch makes a big difference. Air-cooled torches are good for low-amperage tasks. For high-amperage, use water-cooled torches. They prevent overheating.
Choose a torch with a flexible neck. This helps you reach tight spots. Tungsten electrodes are key. Use pure tungsten or zirconiated tungsten for aluminum. The diameter should match your amperage. For 60-80 amps, use 1/16-inch tungsten. For 150-200 amps, use 3/32-inch tungsten.
Use a gas lens for better gas coverage. It helps produce a cleaner weld. A stubby gas lens kit is useful for tight areas.
| Equipment | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Welder Type | AC Capable |
| Amperage Range | 60-200 Amps |
| Gas Type | Argon |
| Flow Rate | 15-20 CFH |
| Torch Type | Air/Water-cooled |
| Tungsten Type | Pure/Zirconiated |
| Tungsten Diameter | 1/16-inch, 3/32-inch |
Selecting The Right Gas
Choosing the right gas for TIG welding aluminum is crucial. The correct gas ensures clean, strong welds and minimizes defects. Let’s explore the types of shielding gas and the benefits of Argon for aluminum welding.
Types Of Shielding Gas
Various shielding gases can be used for TIG welding aluminum. The most common gases include Argon, Helium, and gas mixtures.
- Argon: Pure Argon is the most popular choice for TIG welding aluminum.
- Helium: Sometimes mixed with Argon to improve penetration and heat input.
- Gas Mixtures: Combining Argon and Helium can enhance weld characteristics.
Each gas has its unique benefits and uses. Understanding these can help you select the right gas for your specific needs.
Benefits Of Argon For Aluminum
Argon offers numerous benefits for TIG welding aluminum. It provides excellent arc stability and smooth welds.
- Stability: Argon produces a stable and consistent arc.
- Cleaning Action: Helps remove oxide layers on aluminum surfaces.
- Cost-Effective: Argon is more affordable than other gases.
- Ease of Use: Argon is easy to control, even for beginners.
Using Argon ensures high-quality welds with fewer impurities. This makes it the go-to gas for welding aluminum.
| Gas Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Argon | Stable arc, clean welds, cost-effective | Less penetration |
| Helium | Deeper penetration, increased heat input | Expensive, harder to control |
| Gas Mixtures | Combination of benefits, customizable | Complex setup, cost varies |
Gas Flow Rate
The gas flow rate in TIG welding is crucial for achieving quality welds, especially with aluminum. It affects the cleanliness of the weld and protects the tungsten electrode. Understanding the right flow rate can make a significant difference in your welding outcomes.
Optimal Flow Settings
Setting the optimal gas flow rate is essential. It ensures a stable arc and prevents contamination. Typically, a flow rate between 15 to 20 cubic feet per hour (CFH) works well for aluminum welding. Here’s a simple guide:
| Material Thickness | Gas Flow Rate (CFH) |
|---|---|
| Thin (up to 1/8″) | 15-18 CFH |
| Medium (1/8″ to 1/4″) | 18-20 CFH |
| Thick (over 1/4″) | 20-25 CFH |
Adjusting For Different Conditions
Different conditions require adjustments to your gas flow rate. Factors like wind, joint configuration, and torch angle can impact the flow rate needed. Follow these tips to adjust for varying conditions:
- Windy Environments: Increase the flow rate by 5-10 CFH to prevent contamination.
- Confined Spaces: Reduce the flow rate slightly to avoid turbulence.
- Complex Joints: Adjust based on joint type; fillet welds may need a higher rate.
Always monitor the weld quality and make incremental adjustments. Keeping an eye on the weld pool can help you determine if the flow rate is correct.
Preparation Techniques
Preparing aluminum for TIG welding is crucial. Proper preparation ensures strong, clean welds. Below, we cover essential preparation techniques.
Cleaning The Aluminum
Cleaning aluminum thoroughly is vital. Dirt and oxide layers can cause weld defects.
- Degreasing: Use a solvent like acetone. Wipe the surface to remove oils.
- Oxide Removal: Use a stainless-steel wire brush. Scrub the aluminum to remove the oxide layer.
- Final Cleaning: Clean again with acetone. Ensure no contaminants remain.
Clean tools are essential. Avoid cross-contamination by using dedicated brushes and cloths.
Proper Joint Preparation
Proper joint preparation is key for strong welds. Ensuring the joints fit well is crucial.
- Edge Preparation: Ensure edges are smooth. Use a file or grinder to remove burrs.
- Fit-Up: Ensure a tight fit. Gaps can cause weak welds.
- Alignment: Align the joints properly. Use clamps to hold them in place.
Consider the joint type. Butt joints and lap joints each have specific requirements.
| Joint Type | Preparation Tips |
|---|---|
| Butt Joint | Ensure edges are flush. No gaps should be present. |
| Lap Joint | Overlap should be consistent. Ensure both edges are clean. |
Proper preparation leads to better weld quality. Take your time to prepare each joint carefully.
Welding Techniques
TIG welding aluminum requires specific techniques. Mastering these techniques ensures strong and clean welds.
Establishing The Arc
Establishing the arc is the first step in TIG welding aluminum. Use a tungsten electrode and set the correct polarity. Start with a high frequency for a stable arc.
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Clean the Aluminum | Remove any oxide layer using a wire brush. |
| 2. Set Polarity | Use AC polarity for aluminum welding. |
| 3. Adjust Frequency | Set high frequency to stabilize the arc. |
| 4. Start the Arc | Use a foot pedal to control the arc start. |
Controlling Heat Input
Controlling heat input is crucial for welding aluminum. Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, so it dissipates heat quickly. Use a foot pedal to adjust heat input.
- Start with low heat to avoid burn-through.
- Gradually increase heat as needed.
- Use short welds to manage heat distribution.
- Monitor the weld pool and adjust heat accordingly.
Remember, controlling heat helps prevent warping and ensures a strong weld. Practice these techniques for the best results.
Common Challenges
When performing Tig Welding on aluminum, several challenges can arise. Addressing these issues is crucial for achieving a high-quality weld. This section will explore common challenges such as dealing with contamination and preventing porosity.
Dealing With Contamination
Contamination is a significant problem in Tig Welding aluminum. Aluminum oxide forms quickly on the metal surface. This oxide can prevent proper weld penetration. Use a stainless steel wire brush to clean the aluminum before welding. Ensure the brush is only used on aluminum to avoid cross-contamination.
Oil and grease can also contaminate the weld. Clean the aluminum with acetone or a dedicated aluminum cleaner. Dry the metal completely before starting the weld. Keep the welding area clean and free of dust and debris.
| Contaminant | Cleaning Method |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | Stainless Steel Wire Brush |
| Oil and Grease | Acetone or Aluminum Cleaner |
Preventing Porosity
Porosity occurs when gases get trapped in the weld metal. This can weaken the weld and create defects. To prevent porosity, use high-purity argon gas. Ensure the gas flow rate is appropriate for the welding conditions. A flow rate of 15-20 cubic feet per hour (CFH) is usually sufficient.
Check the welding torch for leaks. Replace any damaged parts to avoid air entering the gas stream. Maintain a consistent torch angle and distance from the weld pool. This helps to create a stable arc and reduce the risk of porosity.
- Use high-purity argon gas
- Ensure correct gas flow rate
- Check for torch leaks
- Maintain consistent torch angle and distance
Proper technique and equipment maintenance are vital for preventing porosity. Regularly inspect and clean your equipment to ensure optimal performance.
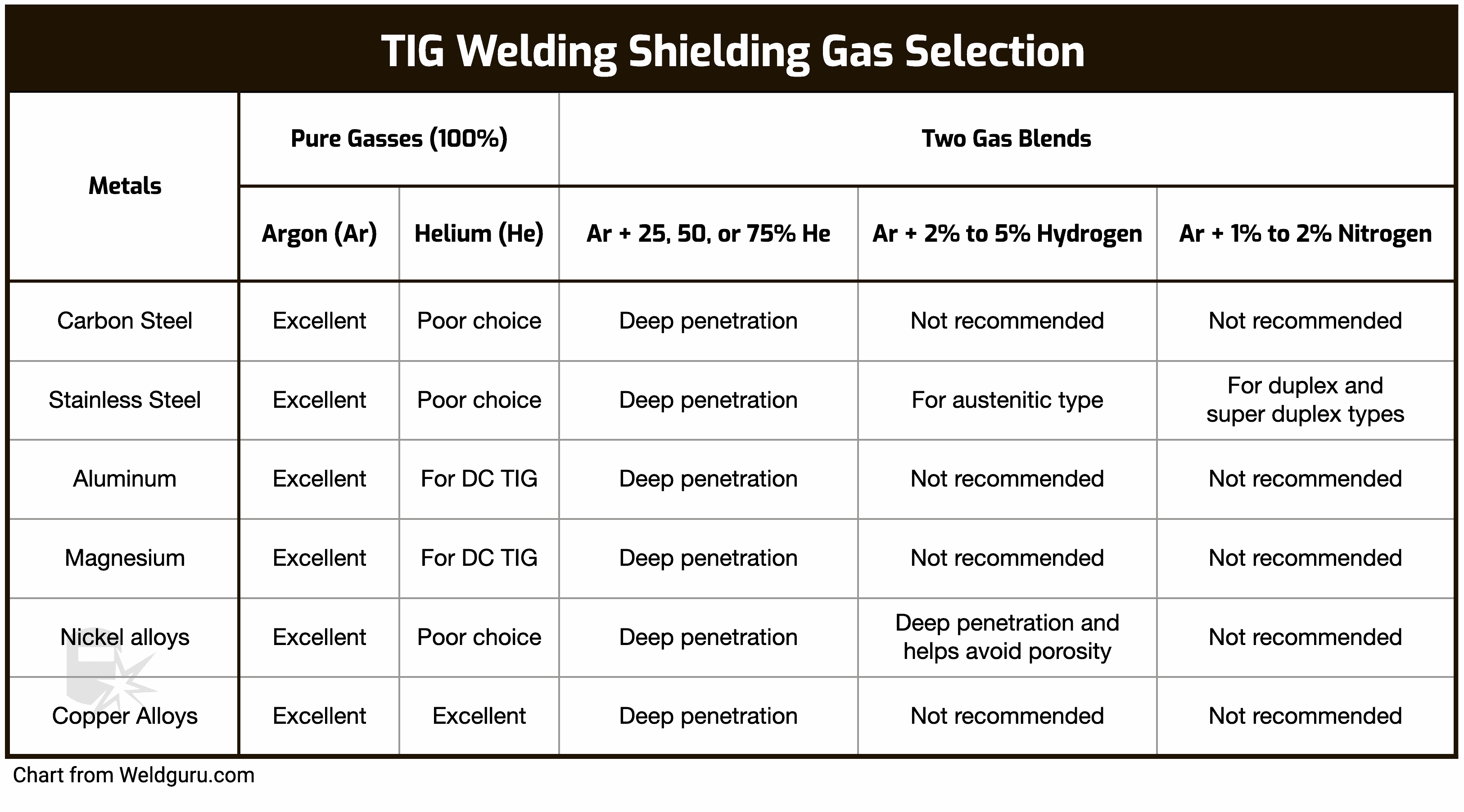
Credit: weldguru.com
Safety Practices
Ensuring safety while performing Tig welding for aluminum is crucial. Proper safety measures protect you from harmful gases and potential accidents. Below are key safety practices to follow.
Protective Gear
Wearing the right protective gear is essential. Here is a list of necessary items:
- Welding Helmet: Use an auto-darkening helmet to protect your eyes.
- Gloves: Wear heat-resistant gloves to shield your hands.
- Jacket: A flame-resistant jacket guards your skin from sparks.
- Boots: Wear steel-toe boots for foot protection.
- Respirator: Use a respirator to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
Safe Handling Of Gas
Handling welding gas safely prevents accidents. Follow these guidelines:
- Storage: Store gas cylinders in a ventilated area.
- Inspection: Regularly check cylinders for leaks.
- Transportation: Secure cylinders during transport.
- Usage: Open valves slowly to avoid pressure surges.
- Ventilation: Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated.
Advanced Tips
Mastering the art of TIG welding aluminum can be challenging. The right gas and techniques make a big difference. Here are some advanced tips to elevate your welding skills.
Pulse Welding Benefits
Pulse welding offers many advantages. It helps control heat input and reduces the risk of burn-through. This is especially important for thin aluminum sheets.
Another benefit of pulse welding is improved weld appearance. It produces consistent and clean weld beads. This makes it ideal for projects where aesthetics matter.
Pulse welding also enhances penetration. This ensures the weld is strong and durable. This can be crucial for structural applications.
- Controls heat input
- Reduces burn-through risk
- Improves weld appearance
- Enhances penetration
Using Backup Gas
Using backup gas can significantly improve weld quality. It helps prevent oxidation on the backside of the weld. This is essential for aluminum, which oxidizes quickly.
The backup gas creates a protective environment. This ensures the weld remains clean and strong. Argon is the most commonly used backup gas.
Setting up a backup gas system is simple. Use a secondary gas line and diffuser. This will cover the backside of the weld with a continuous gas flow.
| Benefits of Backup Gas |
|---|
| Prevents oxidation |
| Ensures clean welds |
| Improves strength |
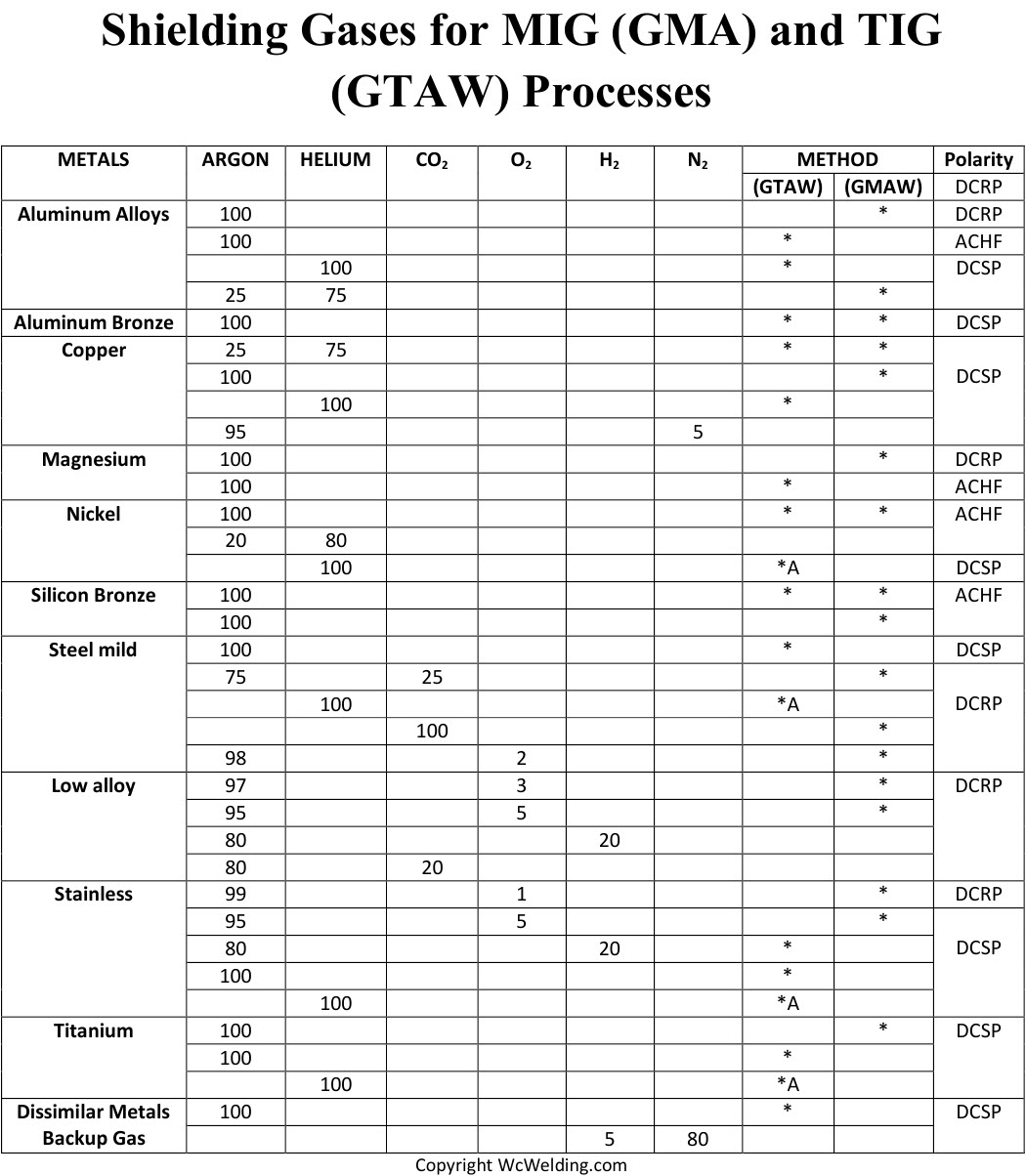
Credit: www.wcwelding.com

Credit: www.perfectwelders.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Gas Is Used For Tig Welding Aluminum?
Argon is the most commonly used gas for TIG welding aluminum. It provides excellent arc stability and cleaning action.
Can You Use Helium For Tig Welding Aluminum?
Yes, helium can be used for TIG welding aluminum. It provides deeper penetration and a hotter arc, but it’s less common.
Why Is Argon Preferred For Aluminum Welding?
Argon is preferred for aluminum welding because it provides good arc stability and excellent cleaning action, ensuring quality welds.
Do You Need A Gas Mix For Aluminum Tig Welding?
No, a pure argon gas is typically used for aluminum TIG welding. Gas mixtures are generally not required.
Conclusion
Choosing the right gas for TIG welding aluminum is crucial. It ensures strong, clean welds every time. Remember to use pure argon for optimal results. This helps prevent contamination and improves weld quality. Perfecting your TIG welding technique takes practice and the right materials.
Happy welding!
